miR‑875‑5p regulates IR and inflammation via targeting TXNRD1 in gestational diabetes rats
- PMID: 33649852
- PMCID: PMC7974266
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11942
miR‑875‑5p regulates IR and inflammation via targeting TXNRD1 in gestational diabetes rats
Abstract
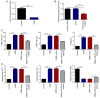
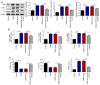
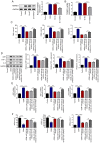
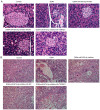
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a serious life‑threatening disease that affects the mother and fetus. However, the pathogenesis of GDM is still unclear. microRNAs (miRs) play vital roles in the regulation of various cell functions. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of miR‑875‑5p and thioredoxin reductase 1 cytoplasmic (TXNRD1) in GDM rats and analyze the associated underlying mechanism. A GDM rat model was induced using an intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. miR‑875‑5p knockdown plasmids or TXNRD1 knockdown plasmids were injected into the rats via the caudal vein. miR‑875‑5p and TXNRD1 expression in the serum were detected using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR (RT‑qPCR) or western blot (WB) analyses. The fasting blood‑glucose (FBG), fasting serum insulin, triglyceride and high density lipoprotein levels were detected by specific commercial kits. The inflammatory response and the induction of oxidative stress were analyzed by assessing the expression of associated markers via WB, RT‑qPCR or commercial kits. The pancreatic and placental injuries were detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining. The results indicated that miR‑875‑5p expression levels were downregulated, whereas TXNRD1 levels were upregulated in GDM rats compared with normal pregnancy rats. miR‑875‑5p significantly regulated TXNRD1 expression in GDM rats. miR‑875‑5p silencing notably reduced FBG and insulin resistance, which was accompanied by reduced expression levels of blood lipid and pro‑inflammatory markers as well as reduced oxidative stress. However, the effects of miR‑875‑5p could be reversed by TXNRD1 silencing. Therefore, the present study indicated that miR‑875‑5p regulated IR and inflammation by targeting TXNRD1 in GDM rats. miR‑875‑5p and TXNRD1 may be considered as potential targets for treating GDM.
Keywords: gestational diabetes mellitus; microRNA‑875‑5p; thioredoxin reductase 1 cytoplasmic; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Metzger BE, Coustan DR, The Organizing Committee Summary and recommendations of the Fourth International Workshop-Conference on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1998;21(Suppl 2):B161–B167. - PubMed
-
- Hajifaraji M, Jahanjou F, Abbasalizadeh F, Aghamohammadzadeh N, Abbasi MM, Dolatkhah N. Effect of probiotic supplements in women with gestational diabetes mellitus on inflammation and oxidative stress biomarkers: A randomized clinical trial. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2018;27:581–591. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

