The role of CYP2D in rat brain in methamphetamine-induced striatal dopamine and serotonin release and behavioral sensitization
- PMID: 33649968
- PMCID: PMC8233297
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-021-05808-9
The role of CYP2D in rat brain in methamphetamine-induced striatal dopamine and serotonin release and behavioral sensitization
Abstract
Rationale: Cytochrome P450 2D (CYP2D) enzymes metabolize many addictive drugs, including methamphetamine. Variable CYP2D metabolism in the brain may alter CNS drug/metabolite concentrations, consequently affecting addiction liability and neuropsychiatric outcomes; components of these can be modeled by behavioral sensitization in rats.
Methods: To investigate the role of CYP2D in the brain in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization, rats were pretreated centrally with a CYP2D irreversible inhibitor (or vehicle) 20 h prior to each of 7 daily methamphetamine (0.5 mg/kg subcutaneous) injections. In vivo brain microdialysis was used to assess brain drug and metabolite concentrations, and neurotransmitter release.
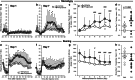
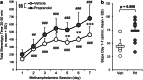
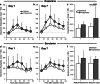
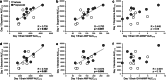
Results: CYP2D inhibitor (versus vehicle) pretreatment enhanced methamphetamine-induced stereotypy response sensitization. CYP2D inhibitor pretreatment increased brain methamphetamine concentrations and decreased the brain p-hydroxylation metabolic ratio. With microdialysis conducted on days 1 and 7, CYP2D inhibitor pretreatment exacerbated stereotypy sensitization and enhanced dopamine and serotonin release in the dorsal striatum. Day 1 brain methamphetamine and amphetamine concentrations correlated with dopamine and serotonin release, which in turn correlated with the stereotypy response slope across sessions (i.e., day 1 through day 7), used as a measure of sensitization.
Conclusions: CYP2D-mediated methamphetamine metabolism in the brain is sufficient to alter behavioral sensitization, brain drug concentrations, and striatal dopamine and serotonin release. Moreover, day 1 methamphetamine-induced neurotransmitter release may be an important predictor of subsequent behavioral sensitization. This suggests the novel contribution of CYP2D in the brain to methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and suggests that the wide variation in human brain CYP2D6 may contribute to differential methamphetamine responses and chronic effects.
Keywords: Behavioral sensitization; CYP2D; Dopamine; Metabolism; Methamphetamine; Microdialysis; Neuropharmacology; Propranolol; Serotonin; Striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
R.F.T has consulted for Quinn Emanuel and Ethismos Research Inc. All other authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nullifying drug-induced sensitization: behavioral and electrophysiological evaluations of dopaminergic and serotonergic ligands in methamphetamine-sensitized rats.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007 Jan 5;86(1):55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.05.014. Epub 2006 Jun 8. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007. PMID: 16762517
-
Neurotoxic regimen of methamphetamine produces evidence of behavioral sensitization in the rat.Synapse. 2001 Jan;39(1):1-7. doi: 10.1002/1098-2396(20010101)39:1<1::AID-SYN1>3.0.CO;2-7. Synapse. 2001. PMID: 11071703
-
Hippocampus norepinephrine, caudate dopamine and serotonin, and behavioral responses to the stereoisomers of amphetamine and methamphetamine.J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1308-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01308.1995. J Neurosci. 1995. PMID: 7869099 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychotoxicity of abused drugs: effects of serotonin receptor ligands on methamphetamine- and cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice.J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Jan;106(1):15-21. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fm0070121. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18198473 Review.
-
Role of brain cytochrome P450 (CYP2D) in the metabolism of monoaminergic neurotransmitters.Pharmacol Rep. 2013;65(6):1519-28. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(13)71513-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24553000 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanowired Delivery of Curcumin Attenuates Methamphetamine Neurotoxicity and Elevates Levels of Dopamine and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;32:385-416. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-32997-5_10. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37480467
-
Nanowired Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Antioxidant Compound H-290/51 Reduces Exacerbation of Methamphetamine Neurotoxicity in Hot Environment.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;32:317-352. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-32997-5_8. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37480465
-
Alterations of Cytochrome P450s and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases in Brain Under Diseases and Their Clinical Significances.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 21;12:650027. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650027. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33967789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CYP2D in the brain impacts oral hydrocodone analgesia in vivo.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Dec 15;221:109291. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109291. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 36241086 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Cytochrome P450: Navigating Neurological Health and Metabolic Regulation.J Xenobiot. 2025 Mar 14;15(2):44. doi: 10.3390/jox15020044. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40126262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bianchetti G, Elghozi JL, Gomeni R, Meyer P, Morselli PL. Kinetics of distribution of di-propranolol in various organs and discrete brain areas of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980;214:682–687. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

