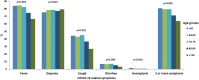
Prevalence of COVID-19-related symptoms by age group
- PMID: 33650071
- PMCID: PMC7919615
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-021-01809-y
Prevalence of COVID-19-related symptoms by age group
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has caused over 95 million confirmed cases of COVID-19 and over 2 million deaths worldwide. According to current literature data, older adults have higher risk of severe disease and mortality due to COVID-19. It is also known that older adults often do not present typical symptoms of diseases. The aim of the study was to assess if the prevalence of typical COVID-19-related symptoms varies by age group.
Methods: Medical charts of a random sample of COVID-19 patients dying in-hospital were retrieved through an integrated national surveillance system and reviewed by a group of researchers at the Italian National Institute of Health. Detailed information on COVID-19-related symptoms were extracted and analyzed.
Results: 3241 confirmed cases of COVID-19-related deaths were identified from 4391 reviewed medical charts. The mean number of COVID-19-related symptoms progressively declined with age, from 2.1 in patients aged < 60 years to 1.7 in those aged 90 years or older (p < 0.001). Moreover, fever, cough, and diarrhea significantly declined with increasing age.
Conclusions: Older adults have atypical presentation of symptoms and may be paucisymptomatic. This may lead to a diagnostic and therapeutic delay which aggravates the prognosis of COVID-19. Special attention should be posed when assessing individuals aged 65 years and older with suspected COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Older adults; SARS-CoV-2; Symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
No financial relationships with any organization that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous 3 years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Centers of Disease and Control and Prevention (2020) Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html. Accessed 23 December 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous