Zymogen-locked mutant prostasin (Prss8) leads to incomplete proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and severely compromises triamterene tolerance in mice
- PMID: 33650216
- PMCID: PMC8159854
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.13640
Zymogen-locked mutant prostasin (Prss8) leads to incomplete proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and severely compromises triamterene tolerance in mice
Abstract
Aim: The serine protease prostasin (Prss8) is expressed in the distal tubule and stimulates proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in co-expression experiments in vitro. The aim of this study was to explore the role of prostasin in proteolytic ENaC activation in the kidney in vivo.
Methods: We used genetically modified knockin mice carrying a Prss8 mutation abolishing proteolytic activity (Prss8-S238A) or a mutation leading to a zymogen-locked state (Prss8-R44Q). Mice were challenged with low sodium diet and diuretics. Regulation of ENaC activity by Prss8-S238A and Prss8-R44Q was studied in vitro using the Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system.
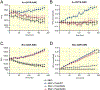
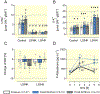
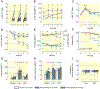
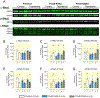
Results: Co-expression of murine ENaC with Prss8-wt or Prss8-S238A in oocytes caused maximal proteolytic ENaC activation, whereas ENaC was activated only partially in oocytes co-expressing Prss8-R44Q. This was paralleled by a reduced proteolytic activity at the cell surface of Prss8-R44Q expressing oocytes. Sodium conservation under low sodium diet was preserved in Prss8-S238A and Prss8-R44Q mice but with higher plasma aldosterone concentrations in Prss8-R44Q mice. Treatment with the ENaC inhibitor triamterene over four days was tolerated in Prss8-wt and Prss8-S238A mice, whereas Prss8-R44Q mice developed salt wasting and severe weight loss associated with hyperkalemia and acidosis consistent with impaired ENaC function and renal failure.
Conclusion: Unlike proteolytically inactive Prss8-S238A, zymogen-locked Prss8-R44Q produces incomplete proteolytic ENaC activation in vitro and causes a severe renal phenotype in mice treated with the ENaC inhibitor triamterene. This indicates that Prss8 plays a role in proteolytic ENaC activation and renal function independent of its proteolytic activity.
Keywords: ENaC; Prostasin; Prss8; Prss8-R44Q; Prss8-S238A; epithelial sodium channel.
© 2021 The Authors. Acta Physiologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Scandinavian Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests:
None.
Figures



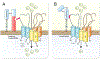
Comment in
-
Non-enzymatic function of prostasin and sodium balance.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021 May;232(1):e13649. doi: 10.1111/apha.13649. Epub 2021 Mar 21. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 33721422 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Kidney-Specific CAP1/Prss8-Deficient Mice Maintain ENaC-Mediated Sodium Balance through an Aldosterone Independent Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6745. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126745. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743186 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium retention in nephrotic syndrome is independent of the activation of the membrane-anchored serine protease prostasin (CAP1/PRSS8) and its enzymatic activity.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Jun;474(6):613-624. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02682-y. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35312839 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of HAI-2 in mice with decreased prostasin activity leads to an early-onset intestinal failure resembling congenital tufting enteropathy.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 4;13(4):e0194660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194660. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29617460 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel and therapeutic application of a serine protease inhibitor for the treatment of salt-sensitive hypertension.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012 Feb;16(1):44-8. doi: 10.1007/s10157-011-0506-1. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22038264 Review.
-
Regulation of renal sodium handling through the interaction between serine proteases and serine protease inhibitors.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2010 Oct;14(5):405-10. doi: 10.1007/s10157-010-0299-7. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20535627 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney-Specific CAP1/Prss8-Deficient Mice Maintain ENaC-Mediated Sodium Balance through an Aldosterone Independent Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6745. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126745. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743186 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of distal tubule sodium transport: mechanisms and roles in homeostasis and pathophysiology.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Aug;474(8):869-884. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02732-5. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35895103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ENaC activation by proteases.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022 May;235(1):e13811. doi: 10.1111/apha.13811. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35276025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of renal epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC) in infants with congenital heart disease.Front Pediatr. 2024 Feb 6;12:1338672. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1338672. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38379911 Free PMC article.
-
The small molecule activator S3969 stimulates the epithelial sodium channel by interacting with a specific binding pocket in the channel's β-subunit.J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):105785. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105785. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38401845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossier BC, Stutts MJ. Activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by serine proteases. Annual review of physiology. 2009;71:361–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

