The prognostic significance of single-nucleotide polymorphism array-based whole-genome analysis and uniparental disomy in myelodysplastic syndrome
- PMID: 33650312
- PMCID: PMC8518839
- DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.13502
The prognostic significance of single-nucleotide polymorphism array-based whole-genome analysis and uniparental disomy in myelodysplastic syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a group of heterogeneous hematological diseases characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and dysplastic morphology. Single nucleotide polymorphism array (SNP-A)-based whole genome analysis has a much higher resolution for chromosomal alterations when compared with conventional cytogenetic tools. In the present study, we evaluated the diagnostic value and prognostic significance of SNP-A in MDS patients with normal karyotypes.
Methods: A total of 127 patients with MDS and myeloproliferative neoplasms or acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes were included in our study. The advantages and disadvantages of SNP-A were compared with those of traditional metaphase cytogenetic analysis (MC). The Kaplan-Meier analysis and COX regression analysis were used to investigate the prognostic value of SNP-A and uniparental disomy (UPD) in MDS patients with normal karyotype. Furthermore, the chromosomal abnormalities detected by SNP-A in patients with specific gene mutations were explored.
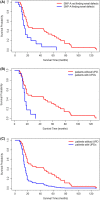
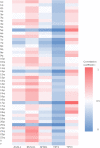
Results: SNP-A was more sensitive toward meaningful chromosomal aberrations (58.2% vs 36.9%; P < .05) than MC. Among the patients with normal karyotype, those who were detected with new chromosomal abnormalities via SNP-A presented with inferior survival compared with those without the abnormalities (P = .003). Additionally, the presence of UPD was an independent prognostic factor in patients with normal karyotype (P = .01). TP53 and RUNX1 mutations often occurred with abnormalities in chromosomes 17p and 21q, respectively.
Conclusions: Compared with MC, SNP-A capable of detecting UPD can offer more diagnostic and prognostic information; TP53 and RUNX1 gene mutations are often accompanied by abnormalities in their chromosomes (17p, 22q).
Keywords: metaphase cytogenetic analysis; myelodysplastic syndrome; uniparental disomy.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The researchers claim no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chromosomal lesions and uniparental disomy detected by SNP arrays in MDS, MDS/MPD, and MDS-derived AML.Blood. 2008 Feb 1;111(3):1534-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-05-092304. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Blood. 2008. PMID: 17954704 Free PMC article.
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism array (SNP-A) improves the identification of chromosomal abnormalities by metaphase cytogenetics in myelodysplastic syndrome.J Clin Pathol. 2017 May;70(5):435-442. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2016-204023. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Clin Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27836923
-
Significance of genome-wide analysis of copy number alterations and UPD in myelodysplastic syndromes using combined CGH - SNP arrays.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(22):3739-47. doi: 10.2174/092986712801661121. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22680919 Review.
-
Combining metaphase cytogenetics with single nucleotide polymorphism arrays can improve the diagnostic yield and identify prognosis more precisely in myelodysplastic syndromes.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):2627-2636. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2125173. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 36148999 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress of cytogenetic detection in myelodysplastic syndromes].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;19(6):1536-40. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22169320 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Bone Marrow Failure Diseases.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022 Feb 27;2022:3528598. doi: 10.1155/2022/3528598. eCollection 2022. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35265454 Free PMC article.
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome presenting with central diabetes insipidus is associated with monosomy 7, visible or hidden: report of two cases and literature review.Mol Cytogenet. 2021 Sep 1;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13039-021-00563-0. Mol Cytogenet. 2021. PMID: 34470671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prchal JT, Throckmorton DW, Carroll AJ 3rd, Fuson EW, Gams RA, Prchal JF. A common progenitor for human myeloid and lymphoid cells. Nature. 1978;274(5671):590‐591. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997;89(6):2079‐2088. - PubMed
-
- Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, et al. New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood. 2007;110(13):4385‐4395. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

