Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio variability and incident diabetes: A 7-year prospective study in a Chinese population
- PMID: 33650324
- PMCID: PMC8504899
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13536
Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio variability and incident diabetes: A 7-year prospective study in a Chinese population
Abstract
Aims/introduction: The correlation between triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio variability and incident diabetes has not been fully elucidated. We aimed to characterize the relationship between TG/HDL-C ratio variability and new-onset diabetes in Chinese adults.
Materials and methods: A total of 45,911 patients with three TG and HDL measurements between 2006 and 2011 were enrolled. Average real variability (ARV) were used to evaluate variability, and participants were grouped according to tertiles of TG/HDL-ARV.
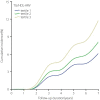
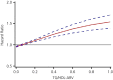
Results: There were 3,724 cases of incident diabetes mellitus during the observation period (6.24 ± 1.2 years). The 7-year cumulative incidences of diabetes mellitus in tertiles 1, 2 and 3 were 6.13%, 8.09% and 11.77%, respectively. New-onset diabetes increased with the tertiles of TG/HDL-ARV. This association was further confirmed after adjustment for mean TG/HDL-C ratio, TG/HDL-C ratio change slope, fasting plasma glucose variability (ARV) and other traditional risk factors for diabetes, the hazard ratio value for incident diabetes was 1.38 (1.25-1.50) for the highest tertile, and risk of diabetes increases by 4% with a one standard deviation increase in TG/HDL-C ratio variability. Restricted cubic splines showed a dose-response relationship between TG/HDL-C ratio variability and incident diabetes. Similar results were obtained in various subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions: High TG/HDL-C variability was associated with a higher risk of diabetes in Chinese adults, independent of the direction of TG/HDL-C variability.
Keywords: Diabetes; Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; Variability.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

