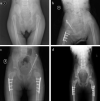
Open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy combined with femoral osteotomy in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Comparison of results before and after the age of 4 years
- PMID: 33650507
- PMCID: PMC7932742
- DOI: 10.5152/j.aott.2021.17385
Open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy combined with femoral osteotomy in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Comparison of results before and after the age of 4 years
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological findings of radical reduction (open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy combined with femoral osteotomy) for children of walking age, younger and older than 4 years in the treatment of with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH).
Methods: In this retrospective study, children of walking age with DDH who underwent radical reduction between 2008 and 2014 were identified. They were then divided into 2 groups according to the age at which the surgery was performed: before and after the age of 4 years. Improvement in the acetabular index was examined on follow-up radiographs. The presence of avascular necrosis (AVN) was determined and classified on the basis of the Kalamchi-MacEwen classification on final follow-up radiographs. Clinical assessment was performed with the modified McKay criteria at the final follow-up appointment.
Results: A total of 19 children (14 girls, 5 boys; mean age=37.5±21 months) (25 hips) were included. Their mean age was 27.9±4.9 and 63.3±19.7 months in children operated before and after the age of 4 years, respectively. The mean follow-up time was 29.9±19 and 19.6±5 months in children operated before and after the age of 4 years, respectively. No significant difference was observed in improvements in the acetabular index between children younger than 4 years (24±6.9°) and those older than 4 years (20.7±6.7°) (p=0.25). According to the modified McKay criteria, all the children younger than 4 years exhibited excellent or good clinical results compared with those operated after the age of 4 years (67%) (p=0.013). At the final follow-up, 64% of all patients demonstrated no radiographical sign of AVN. The rates of AVN were significantly higher in children operated after the age of 4 years (33%) than in those operated before the age of 4 years (19%) (p=0.049).
Conclusion: Better clinical and radiographical results can be expected from radical reduction in children undergoing surgery before the age of 4 years.
Level of evidence: level III, Therapeutic Study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salter osteotomy without open reduction in the Tönnis type II developmental hip dysplasia: A retrospective clinical study.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019 Jan-Apr;27(1):2309499019835572. doi: 10.1177/2309499019835572. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019. PMID: 30879389
-
Radiological and clinical outcomes of medial approach open reduction by using two intervals in developmental dysplasia of the hip.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018 Mar;52(2):81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.aott.2018.01.006. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018. PMID: 29454563 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and radiological outcomes of combined acetabuloplasty with acetabular redirectional osteotomy and femoral shortening for children older than 9 years of age with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a retrospective case series.J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020 Sep;29(5):417-423. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000774. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2020. PMID: 32694431
-
How Does Bony Surgery Affect Results of Anterior Open Reduction in Walking-age Children With Developmental Hip Dysplasia?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 May;474(5):1199-208. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4598-x. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26487045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dega transiliac pelvic osteotomy for developmental hip dysplasia: a systematic review.J Pediatr Orthop B. 2023 May 1;32(3):211-220. doi: 10.1097/BPB.0000000000000784. Epub 2022 Sep 11. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2023. PMID: 32932416
Cited by
-
Efficacy of a Graftless Salter Osteotomy in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip.J Pediatr Soc North Am. 2025 Mar 28;11:100188. doi: 10.1016/j.jposna.2025.100188. eCollection 2025 May. J Pediatr Soc North Am. 2025. PMID: 40432865 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on Salter osteotomy combined with subtrochanteric shortening and derotational osteotomy in treatment of Tönnis type Ⅲ and Ⅳ developmental dysplasia of the hip in children].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 15;39(2):168-173. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202408069. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39971362 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- JAH, editor. Tachdjian’s Pediatric Orthopaedics. 4th ed. Saunders; 2008. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials