Targeting the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) to treat autoimmune diseases and maternal-fetal immune cytopenias
- PMID: 33650699
- PMCID: PMC8186400
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.16341
Targeting the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) to treat autoimmune diseases and maternal-fetal immune cytopenias
Abstract
FcRn, a non-classical Fc gamma (γ) receptor (FcγR) with near ubiquitous expression, plays key roles in disease pathogenesis and progression though immunoglobulin G (IgG) transport, IgG recycling, and IgG-immune complex clearance. FcRn function can be inhibited using IgG-based and non-IgG-based antagonists, by exploiting the pH-dependent binding affinity of FcRn for the IgG Fc region. FcRn therapeutics have shown promise in murine models and human clinical trials for autoimmune diseases and maternal-fetal immune cytopenias; they appear safe, well-tolerated, and reduce circulating IgG levels. Compared to traditional therapeutics, inhibiting FcRn has fewer adverse side effects and represents a new approach that is less invasive, time-consuming, and costly.
Keywords: AIHA/drug-induced IHA; HDN; immune thrombocytopenia.
© 2021 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
COI: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
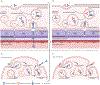
References
-
- Giacomelli R, Afeltra A, Alunno A, et al. International consensus: What else can we do to improve diagnosis and therapeutic strategies in patients affected by autoimmune rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritides, systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome and Sjogren’s syndrome)?: The unmet needs and the clinical grey zone in autoimmune disease management. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(9):911–924. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.07.012 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

