Association of Toll-like receptor 7 variants with life-threatening COVID-19 disease in males: findings from a nested case-control study
- PMID: 33650967
- PMCID: PMC7987337
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67569
Association of Toll-like receptor 7 variants with life-threatening COVID-19 disease in males: findings from a nested case-control study
Abstract
Background: Recently, loss-of-function variants in TLR7 were identified in two families in which COVID-19 segregates like an X-linked recessive disorder environmentally conditioned by SARS-CoV-2. We investigated whether the two families represent the tip of the iceberg of a subset of COVID-19 male patients.
Methods: This is a nested case-control study in which we compared male participants with extreme phenotype selected from the Italian GEN-COVID cohort of SARS-CoV-2-infected participants (<60 y, 79 severe cases versus 77 control cases). We applied the LASSO Logistic Regression analysis, considering only rare variants on young male subsets with extreme phenotype, picking up TLR7 as the most important susceptibility gene.
Results: Overall, we found TLR7 deleterious variants in 2.1% of severely affected males and in none of the asymptomatic participants. The functional gene expression profile analysis demonstrated a reduction in TLR7-related gene expression in patients compared with controls demonstrating an impairment in type I and II IFN responses.
Conclusions: Young males with TLR7 loss-of-function variants and severe COVID-19 represent a subset of male patients contributing to disease susceptibility in up to 2% of severe COVID-19.
Funding: Funded by private donors for the Host Genetics Research Project, the Intesa San Paolo for 2020 charity fund, and the Host Genetics Initiative.
Clinical trial number: NCT04549831.
Keywords: COVID-19; LASSO Logistic Regression Analysis; TLR7; genetics; genomics; human; medicine.
© 2021, Fallerini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CF, SD, SM, EB, NP, DF, FP, ES, MB, FF, MP, SL, FC, EQ, MV, SR, MS, MB, OS, KC, SF, FM, AR, MM, EF No competing interests declared
Figures
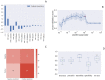
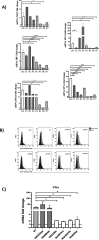
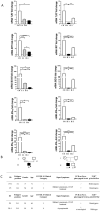
 ).
).Comment in
-
Rare variants increase the risk of severe COVID-19.Elife. 2021 Mar 23;10:e67860. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67860. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33752797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastard P, Rosen LB, Zhang Q, Michailidis E, Hoffmann HH, Zhang Y, Dorgham K, Philippot Q, Rosain J, Béziat V, Manry J, Shaw E, Haljasmägi L, Peterson P, Lorenzo L, Bizien L, Trouillet-Assant S, Dobbs K, de Jesus AA, Belot A, Kallaste A, Catherinot E, Tandjaoui-Lambiotte Y, Le Pen J, Kerner G, Bigio B, Seeleuthner Y, Yang R, Bolze A, Spaan AN, Delmonte OM, Abers MS, Aiuti A, Casari G, Lampasona V, Piemonti L, Ciceri F, Bilguvar K, Lifton RP, Vasse M, Smadja DM, Migaud M, Hadjadj J, Terrier B, Duffy D, Quintana-Murci L, van de Beek D, Roussel L, Vinh DC, Tangye SG, Haerynck F, Dalmau D, Martinez-Picado J, Brodin P, Nussenzweig MC, Boisson-Dupuis S, Rodríguez-Gallego C, Vogt G, Mogensen TH, Oler AJ, Gu J, Burbelo PD, Cohen JI, Biondi A, Bettini LR, D'Angio M, Bonfanti P, Rossignol P, Mayaux J, Rieux-Laucat F, Husebye ES, Fusco F, Ursini MV, Imberti L, Sottini A, Paghera S, Quiros-Roldan E, Rossi C, Castagnoli R, Montagna D, Licari A, Marseglia GL, Duval X, Ghosn J, Tsang JS, Goldbach-Mansky R, Kisand K, Lionakis MS, Puel A, Zhang SY, Holland SM, Gorochov G, Jouanguy E, Rice CM, Cobat A, Notarangelo LD, Abel L, Su HC, Casanova JL, HGID Lab, NIAID-USUHS Immune Response to COVID Group, COVID Clinicians, COVID-STORM Clinicians, Imagine COVID Group, French COVID Cohort Study Group, Milieu Intérieur Consortium, CoV-Contact Cohort, Amsterdam UMC Covid-19 Biobank, COVID Human Genetic Effort, Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 2020;370:eabd4585. doi: 10.1126/science.abd4585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Daga S, Fallerini C, Baldassarri M, Fava F, Valentino F, Doddato G, Benetti E, Furini S, Giliberti A, Tita R, Amitrano S, Bruttini M, Meloni I, Pinto AM, Raimondi F, Stella A, Biscarini F, Picchiotti N, Gori M, Pinoli P, Ceri S, Sanarico M, Crawley FP, Birolo G, Renieri A, Mari F, Frullanti E, GEN-COVID Multicenter Study Employing a systematic approach to biobanking and analyzing clinical and genetic data for advancing COVID-19 research. European Journal of Human Genetics. 2021;1:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41431-020-00793-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garg S, Kim L, Whitaker M, O'Halloran A, Cummings C, Holstein R, Prill M, Chai SJ, Kirley PD, Alden NB, Kawasaki B, Yousey-Hindes K, Niccolai L, Anderson EJ, Openo KP, Weigel A, Monroe ML, Ryan P, Henderson J, Kim S, Como-Sabetti K, Lynfield R, Sosin D, Torres S, Muse A, Bennett NM, Billing L, Sutton M, West N, Schaffner W, Talbot HK, Aquino C, George A, Budd A, Brammer L, Langley G, Hall AJ, Fry A. Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 - COVID-NET, 14 states, march 1-30, 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2020;69:458–464. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- D.L. n 18 of March 17/Private Donors for Host Genetics Research Project
- N.B.2020/0119/Intesa San Paolo for 2020 charity fund
- Dipartimenti di Eccellenza 2018-2020/Host Genetics Initiative
- Dipartimenti di Eccellenza 2018-2020/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca
- Bando Ricerca COVID-19 Toscana/Regione Toscana
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

