Mechanics informed fluoroscopy of esophageal transport
- PMID: 33651206
- PMCID: PMC8159889
- DOI: 10.1007/s10237-021-01420-0
Mechanics informed fluoroscopy of esophageal transport
Abstract
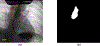
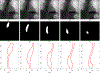
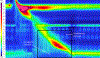
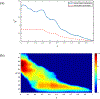
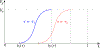
Fluoroscopy is a radiographic procedure for evaluating esophageal disorders such as achalasia, dysphasia and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It performs dynamic imaging of the swallowing process and provides anatomical detail and a qualitative idea of how well swallowed fluid is transported through the esophagus. In this work, we present a method called mechanics informed fluoroscopy (FluoroMech) that derives patient-specific quantitative information about esophageal function. FluoroMech uses a convolutional neural network to perform segmentation of image sequences generated from the fluoroscopy, and the segmented images become input to a one-dimensional model that predicts the flow rate and pressure distribution in fluid transported through the esophagus. We have extended this model to identify and estimate potential physiomarkers such as esophageal wall stiffness and active relaxation ahead of the peristaltic wave in the esophageal musculature. FluoroMech requires minimal computational time and hence can potentially be applied clinically in the diagnosis of esophageal disorders.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Esophageal active relaxation; Esophageal wall stiffness; Flexible tube; Image segmentation; One-dimensional flow.
Figures


References
-
- Abadi Martín, Agarwal Ashish, Barham Paul, Brevdo Eugene, Chen Zhifeng, Citro Craig, Corrado Greg S., Davis Andy, Dean Jeffrey, Devin Matthieu, Ghemawat Sanjay, Goodfellow Ian, Harp Andrew, Irving Geoffrey, Isard Michael, Jia Yangqing, Jozefowicz Rafal, Kaiser Lukasz, Kudlur Manjunath, Levenberg Josh, Dan Mané Rajat Monga, Moore Sherry, Murray Derek, Olah Chris, Schuster Mike, Shlens Jonathon, Steiner Benoit, Sutskever Ilya, Talwar Kunal, Tucker Paul, Vanhoucke Vincent, Vasudevan Vijay, Fernanda Viégas Oriol Vinyals, Warden Pete, Wattenberg Martin, Wicke Martin, Yu Yuan, and Zheng Xiaoqiang. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems, 2015. Software available from tensorflow.org.
-
- Brasseur James G.. A fluid mechanical perspective on esophageal bolus transport. Dysphagia, 2(1):32, March 1987. - PubMed
-
- Chollet François et al. Keras. https://keras.io, 2015.
-
- Ciresan Dan, Giusti Alessandro, Gambardella Luca M., and Schmidhuber Jürgen. Deep neural networks segment neuronal membranes in electron microscopy images. In Pereira F, Burges CJC, Bottou L, and Weinberger KQ, editors, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25, pages 2843–2851. Curran Associates, Inc., 2012.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

