Deregulated miRNA expression is associated with endothelial dysfunction in post-mortem lung biopsies of COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 33651636
- PMCID: PMC7938642
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00457.2020
Deregulated miRNA expression is associated with endothelial dysfunction in post-mortem lung biopsies of COVID-19 patients
Abstract
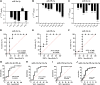
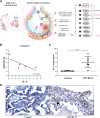
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are critical modulators of endothelial homeostasis, which highlights their involvement in vascular diseases, including those caused by virus infections. Our main objective was to identify miRNAs involved in the endothelial function and determine their expression in post-mortem lung biopsies of COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory injuries and thrombotic events. Based on functional enrichment analysis, miR-26a-5p, miR-29b-3p, and miR-34a-5p were identified as regulators of mRNA targets involved in endothelial and inflammatory signaling pathways, as well as viral diseases. A miRNA/mRNA network, constructed based on protein-protein interactions of the miRNA targets and the inflammatory biomarkers characterized in the patients, revealed a close interconnection of these miRNAs in association to the endothelial activation/dysfunction. Reduced expression levels of selected miRNAs were observed in the lung biopsies of COVID-19 patients (n = 9) compared to the Controls (n = 10) (P < 0.01-0.0001). MiR-26a-5p and miR-29b-3p presented the best power to discriminate these groups (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.8286, and AUC = 0.8125, respectively). The correlation analysis of the miRNAs with inflammatory biomarkers in the COVID-19 patients was significant for miR-26a-5p [IL-6 (r2 = 0.5414), and ICAM-1 (r2 = 0.5624)], and miR-29b-3p [IL-4 (r2 = 0.8332) and IL-8 (r2 = 0.2654)]. Altogether, these findings demonstrate the relevance and the non-random involvement of miR-26a-5p, miR-29b-3p, and miR-34a-5p in endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory response in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection and the occurrence of severe lung injury and immunothrombosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; endothelial dysfunction; lung injuries; microRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, Vanstapel A, Werlein C, Stark H, Tzankov A, Li WW, Li VW, Mentzer SJ, Jonigk D. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med 383: 120–128, 2020. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, Liu S, Zhao P, Liu H, Zhu L, Tai Y, Bai C, Gao T, Song J, Xia P, Dong J, Zhao J, Wang FS. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med 8: 420–422, 2020. [Erratum inLancetRespir Med. 8: e26; 2020]. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, Müller MA, Drosten C, Pöhlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181: 271–280, 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

