A systematic literature review of herpes zoster incidence worldwide
- PMID: 33651654
- PMCID: PMC8115759
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1847582
A systematic literature review of herpes zoster incidence worldwide
Abstract
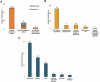
We conducted a systematic review to characterize the incidence rate of herpes zoster (HZ) in the general population, specifically in individuals ≥50 years of age. A total of 69 publications were included in the review. We found a cumulative incidence of HZ ranging from 2.9-19.5 cases per 1,000 population and an incidence rate of HZ ranging from 5.23-10.9 cases per 1,000 person-years. The cumulative incidence (3.22-11.2 versus 2.44-8.0 cases per 1,000 population) and incidence rates (6.05-12.8 versus 4.30-8.5 cases per 1,000 person-years) were higher in females than males. Studies revealed a trend of increasing incidence of HZ with increasing age and over time. Variations in incidence estimates can be attributed to the various study designs, case ascertainments, age distributions of the population and year of the study. HZ is associated with a substantial disease burden and is expected to increase due to population aging.
Keywords: Incidence; adults; epidemiology; herpes zoster; review; shingles; vaccination.
Figures




References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Shingles (herpes zoster) overview. 2018. Accessed 2020 April28. https://www.cdc.gov/shingles/about/index.html
-
- Harpaz R, Ortega-Sanchez IR, Seward JF.. Advisory committee on immunization practices centers for disease c, prevention. prevention of herpes zoster: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57:1–30. quiz CE32-34. - PubMed
-
- Drolet M, Brisson M, Levin MJ, Schmader KE, Oxman MN, Johnson RW, Camden S, Mansi JA. A prospective study of the herpes zoster severity of illness. Clin J Pain. 2010;26:656–66. - PubMed
-
- Volpi A. Severe complications of herpes zoster. Herpes. 2007;14:35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
