Germ cell differentiation requires Tdrd7-dependent chromatin and transcriptome reprogramming marked by germ plasm relocalization
- PMID: 33651978
- PMCID: PMC7957325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.007
Germ cell differentiation requires Tdrd7-dependent chromatin and transcriptome reprogramming marked by germ plasm relocalization
Abstract
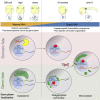
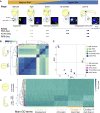
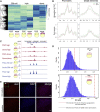
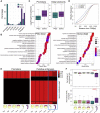
In many animal models, primordial germ cell (PGC) development depends on maternally deposited germ plasm, which prevents somatic cell fate. Here, we show that PGCs respond to regulatory information from the germ plasm in two distinct phases using two distinct mechanisms in zebrafish. We demonstrate that PGCs commence zygotic genome activation together with the somatic blastocysts with no demonstrable differences in transcriptional and chromatin opening. Unexpectedly, both PGC and somatic blastocysts activate germ-cell-specific genes, which are only stabilized in PGCs by cytoplasmic germ plasm determinants. Disaggregated perinuclear relocalization of germ plasm during PGC migration is regulated by the germ plasm determinant Tdrd7 and is coupled to dramatic divergence between PGC and somatic transcriptomes. This transcriptional divergence relies on PGC-specific cis-regulatory elements characterized by promoter-proximal distribution. We show that Tdrd7-dependent reconfiguration of chromatin accessibility is required for elaboration of PGC fate but not for PGC migration.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; DNA methylation; RNA-seq; ZGA; buckyball; chromatin; dazl; germ granules; primordial germ cells; transcription.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Andrey G., Mundlos S. The three-dimensional genome: regulating gene expression during pluripotency and development. Development. 2017;144:3646–3658. - PubMed
-
- Bender L.B., Cao R., Zhang Y., Strome S. The MES-2/MES-3/MES-6 complex and regulation of histone H3 methylation in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:1639–1643. - PubMed
-
- Blaser H., Eisenbeiss S., Neumann M., Reichman-Fried M., Thisse B., Thisse C., Raz E. Transition from non-motile behaviour to directed migration during early PGC development in zebrafish. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:4027–4038. - PubMed
-
- Bogdanovic O., Fernandez-Miñán A., Tena J.J., de la Calle-Mustienes E., Hidalgo C., van Kruysbergen I., van Heeringen S.J., Veenstra G.J., Gómez-Skarmeta J.L. Dynamics of enhancer chromatin signatures mark the transition from pluripotency to cell specification during embryogenesis. Genome Res. 2012;22:2043–2053. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

