Osteopontin mRNA expression by rat mesothelial cells exposed to multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a potential biomarker of chronic neoplastic transformation in vitro
- PMID: 33652123
- PMCID: PMC8085121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105126
Osteopontin mRNA expression by rat mesothelial cells exposed to multi-walled carbon nanotubes as a potential biomarker of chronic neoplastic transformation in vitro
Abstract
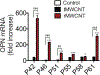
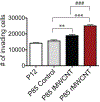
Mesothelioma is a cancer of the lung pleura primarily associated with inhalation of asbestos fibers. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are engineered nanomaterials that pose a potential risk for mesothelioma due to properties that are similar to asbestos. Inhaled MWCNTs migrate to the pleura in rodents and some types cause mesothelioma. Like asbestos, there is a diversity of MWCNT types. We investigated the neoplastic potential of tangled (tMWCNT) versus rigid (rMWCNT) after chronic exposure using serial passages of rat mesothelial cells in vitro. Normal rat mesothelial (NRM2) cells were exposed to tMWCNTs or rMWCNTs for 45 weeks over 85 passages to determine if exposure resulted in transformation to a neoplastic phenotype. Rat mesothelioma (ME1) cells were used as a positive control. Osteopontin (OPN) mRNA was assayed as a biomarker of transformation by real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and transformation was determined by a cell invasion assay. Exposure to rMWCNTs, but not tMWCNTs, resulted in transformation of NRM2 cells into an invasive phenotype that was similar to ME1 cells. Moreover, exposure of NRM2 cells to rMWCNTs increased OPN mRNA that correlated with cellular transformation. These data suggest that OPN is a potential biomarker that should be further investigated to screen the carcinogenicity of MWCNTs in vitro.
Keywords: Carbon nanotubes; Mesothelial cells; Mesothelioma; Osteopontin.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


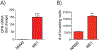
References
-
- Amany FM, Mohamed NA, El-Ghamry R, Brik A, Salem AM, Shoukry A, El-Sebaey A 2013. Mesothelin and osteopontin as diagnostic and prognostic markers of malignant pleural mesothelioma in Egyptian patients undergoing pleurodesis. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc 62, 115–120. 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2013.04.005 - DOI
-
- Boyles MSP, Young L, Brown DM, MacCalman L, Cowie H, Moisala A, Smail F, Smith PJW, Proudfoot L, Windle AH, Stone V 2015. Multi-walled carbon nanotube induced frustrated phagocytosis, cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory conditions in macrophages are length dependent and greater than that of asbestos. Toxicol. Vitr 29, 1513–1528. 10.1016/J.TIV.2015.06.012 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

