Zinc Metalloproteins in Epigenetics and Their Crosstalk
- PMID: 33652690
- PMCID: PMC7996840
- DOI: 10.3390/life11030186
Zinc Metalloproteins in Epigenetics and Their Crosstalk
Abstract
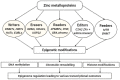
More than half a century ago, zinc was established as an essential micronutrient for normal human physiology. In silico data suggest that about 10% of the human proteome potentially binds zinc. Many proteins with zinc-binding domains (ZBDs) are involved in epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, which regulate transcription in physiological and pathological conditions. Zinc metalloproteins in epigenetics are mainly zinc metalloenzymes and zinc finger proteins (ZFPs), which are classified into writers, erasers, readers, editors, and feeders. Altogether, these classes of proteins engage in crosstalk that fundamentally maintains the epigenome's modus operandi. Changes in the expression or function of these proteins induced by zinc deficiency or loss of function mutations in their ZBDs may lead to aberrant epigenetic reprogramming, which may worsen the risk of non-communicable chronic diseases. This review attempts to address zinc's role and its proteins in natural epigenetic programming and artificial reprogramming and briefly discusses how the ZBDs in these proteins interact with the chromatin.
Keywords: epigenetics; epigenome; zinc finger domain; zinc finger motif; zinc finger proteins; zinc metalloproteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Metalloenzymes.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(15):2748-2785. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180706105903. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29984644 Review.
-
Step out of the groove: epigenetic gene control systems and engineered transcription factors.Adv Genet. 2006;56:163-204. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2660(06)56005-5. Adv Genet. 2006. PMID: 16735158 Review.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
-
Phosphorylation of epigenetic "readers, writers and erasers": Implications for developmental reprogramming and the epigenetic basis for health and disease.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;118(1-2):8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25841987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-terminal in Sp1-like artificial zinc-finger proteins plays crucial roles in determining their DNA binding affinity.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Dec 1;13:106. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-106. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24289163 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
One carbon metabolism supplementation in maturation medium but not embryo culture medium improves the yield of blastocysts from bovine oocytes.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 22;15(1):2749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85410-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39837964 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Current State of Magnetic Force Microscopy to Unravel the Magnetic Properties of Nanomaterials Applied in Biological Systems and Future Directions for Quantum Technologies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 18;13(18):2585. doi: 10.3390/nano13182585. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An insight into the mechanisms of action of selected bioactive compounds against epigenetic targets of prostate cancer: implications on histones modifications.In Silico Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 15;11(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s40203-023-00148-2. eCollection 2023. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37073308 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent and transient olfactory deficits in COVID-19 are associated to inflammation and zinc homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1148595. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1148595. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520523 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of metal transporter Zip14 reduces major histocompatibility complex II expression in murine small intestinal epithelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 7;122(1):e2422321121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2422321121. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39793074 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

