The effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on TGF-β and IL-17 serum levels in migraineurs: post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 33653409
- PMCID: PMC7927391
- DOI: 10.1186/s40780-021-00192-0
The effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on TGF-β and IL-17 serum levels in migraineurs: post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Although the exact mechanism involved in migraine pathogenesis remained uncertain, and different researches have been developed to address the role of neuroinflammation and immune dysfunction. Therefore, considering the immune protective functions of vitamin D3, we aimed to investigate the effects of daily administration of 2000 IU D3 supplements on serum status of immune markers in migraine patients.
Methods and materials: Eighty episodic migraineurs who randomly assigned into two equal groups to receive either vitamin D3 2000 IU/d or placebo for 12-week were enrolled in this placebo-controlled double-blind trial included. Serum concentrations of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and interleukin (IL)-17 were evaluated at baseline and after the trial via the ELISA method.
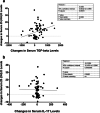
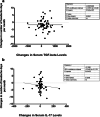
Results: Applying ANCOVA adjusted for baseline levels and confounding variables, it was found that the serum level of TGF-β was significantly higher in vitamin D group (adjusted mean:1665.50 ng/L) than the placebo group (1361.90 ng/L) after the experiment (P-value = 0.012); on the other hand, vitamin D prevented the increment in IL-17 serum level in the intervention group after the trial (adjusted mean:37.84 ng/L) comparing to the controls (adjusted mean:70.09 ng/L; P-value = 0.039). The Pearson correlation analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between changes in serum 25-hydroxy-vitamin D (25(OH)D) and TGF-β (r = - 0.306, P-value = 0.008). In contrast, no significant correlations were noted between serum 25(OH) D and IL-17 changes throughout the study.
Conclusion: Based on the results of this study, it was revealed that 12-week vitamin D3 supplementation (2000 IU/day) could enhance the Th17/Treg related cytokines balance in episodic migraineurs. Although these findings are promising, it is needed to be extended.
Trial registration: The trial is registered in the Iranian registry of clinical trials (IRCT) at 11 July 2018, with IRCT code: IRCT20151128025267N6 ( https://www.irct.ir/trial/31246 ).
Keywords: Cholecalciferol; Headache; Immune cells; Th17/Treg cytokines; Vitamin D3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Chang C-C, Wu C-H, Liu L-K, Chou R-H, Kuo C-S, Huang P-H, Chen L-K, Lin S-J. Association between serum uric acid and cardiovascular risk in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic individuals: the Taiwan I-Lan longitudinal aging study. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22997-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

