Inhibition of HERV-K (HML-2) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients on antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 33653604
- PMCID: PMC8009857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.117358
Inhibition of HERV-K (HML-2) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients on antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
Reactivation of Human Endogenous Retrovirus K (HERV-K), subtype HML-2, has been associated with pathophysiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). We aimed to assess the efficacy of antiretroviral therapy in inhibiting HML-2 in patients with ALS and a possible association between the change in HML-2 levels and clinical outcomes. We studied the effect of 24-weeks antiretroviral combination therapy with abacavir, lamivudine, and dolutegravir on HML-2 levels in 29 ALS patients. HML-2 levels decreased progressively over 24 weeks (P = 0.001) and rebounded within a week of stopping medications (P = 0.02). The majority of participants (82%), defined as "responders", experienced a decrease in HML-2 at week 24 of treatment compared to the pre-treatment levels. Differences in the evolution of some of the clinical outcomes could be seen between responders and non-responders: FVC decreased 23.69% (SE = 11.34) in non-responders and 12.71% (SE = 8.28) in responders. NPI score decreased 91.95% (SE = 6.32) in non-responders and 53.05% (SE = 10.06) in responders (P = 0.01). Thus, participants with a virological response to treatment showed a trend for slower progression of the illness. These findings further support the possible involvement of HML-2 in the clinical course of the disease.
Keywords: ALS; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Antiretroviral; HERV-K; HML-2.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
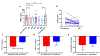
Comment in
-
HERV-K inactive or potential pathogens from within?J Neurol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;423:117359. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.117359. Epub 2021 Feb 20. J Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33640108 No abstract available.
References
-
- McCormick AL, Brown RH Jr., Cudkowicz ME, Al-Chalabi A Garson JA. Quantification of reverse transcriptase in ALS and elimination of a novel retroviral candidate. Neurology 2008;70:278–283. - PubMed
-
- Steele AJ, Al-Chalabi A, Ferrante K, Cudkowicz ME, Brown RH Jr., Garson JA. Detection of serum reverse transcriptase activity in patients with ALS and unaffected blood relatives. Neurology 2005;64:454–458. - PubMed
-
- Andrews WD, Tuke PW, Al-Chalabi A, et al. Detection of reverse transcriptase activity in the serum of patients with motor neurone disease. J Med Virol 2000;61:527–532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

