LRP1B mutations are associated with favorable outcomes to immune checkpoint inhibitors across multiple cancer types
- PMID: 33653800
- PMCID: PMC7929846
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001792
LRP1B mutations are associated with favorable outcomes to immune checkpoint inhibitors across multiple cancer types
Abstract
Background: Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1b (encoded by LRP1B) is a putative tumor suppressor, and preliminary evidence suggests LRP1B-mutated cancers may have improved outcomes with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI).
Methods: We conducted a multicenter, retrospective pan-cancer analysis of patients with LRP1B alterations treated with ICI at Duke University, Johns Hopkins University (JHU) and University of Michigan (UM). The primary objective was to assess the association between overall response rate (ORR) to ICI and pathogenic or likely pathogenic (P/LP) LRP1B alterations compared with LRP1B variants of unknown significance (VUS). Secondary outcomes were the associations with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) by LRP1B status.
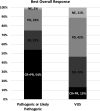
Results: We identified 101 patients (44 Duke, 35 JHU, 22 UM) with LRP1B alterations who were treated with ICI. The most common tumor types by alteration (P/LP vs VUS%) were lung (36% vs 49%), prostate (9% vs 7%), sarcoma (5% vs 7%), melanoma (9% vs 0%) and breast cancer (3% vs 7%). The ORR for patients with LRP1B P/LP versus VUS alterations was 54% and 13%, respectively (OR 7.5, 95% CI 2.9 to 22.3, p=0.0009). P/LP LRP1B alterations were associated with longer PFS (HR 0.42, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.68, p=0.0003) and OS (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.39 to 1.01, p=0.053). These results remained consistent when excluding patients harboring microsatellite instability (MSI) and controlling for tumor mutational burden (TMB).
Conclusions: This multicenter study shows significantly better outcomes with ICI therapy in patients harboring P/LP versus VUS LRP1B alterations, independently of TMB/MSI status. Further mechanistic and prospective validation studies are warranted.
Keywords: genetic markers; immunotherapy; lung neoplasms; prostatic neoplasms.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JZ: consulting: NGM Biopharmaceuticals, UroToday; Travel Expenses: UroToday. RTG: speakers bureau: Bayer Pharma AG; Consulting Fees: Bayer Pharma AG, Invivo Corp, Bard. TZ: research funding: AstraZeneca, Janssen, OmniSeq, PGDx, Pfizer, Merrimack, AbbVie/Stemcentrx, Novartis, Merck, Mirati and Regeneron; Advisory/consultant role: Genentech Roche, Exelixis, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Janssen, Foundation Medicine, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Pharmacyclics and Seattle Genetics; speakers bureau: Genentech Roche, Exelixis, Sanofi-Aventis, Genomic Health; Stocks/Employment: Capio Biosciences (spouse), Archimmune Therapeutics (spouse). MH: consultant: AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Genentech, Janssen, Pfizer; speakers bureau: Exelixis and Genentech; Research Funding (to institution): Acerta, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis, Exelixis, Genentech, Merck, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics. DG: Acerta Pharmaceuticals—Research, American Association for Cancer Research—Sr Editor, Astellas—Consultant, Research, Advisory Board, AstraZeneca—Consultant, Advisory Board, Axess Oncology—Independent Contractor, Bayer H/C Pharmaceuticals—Research, Consultant, Speaker, Honorarium, Travel accommodations, SC, Bristol-Myers Squibb—Consultant, Research, Steering Committee, Calithera—Research, Capio Biosciences—Scientific Advisory Board, EMD Serono—Honorarium, Exelixis, Inc—Research, Consultant, Speaker, Honorarium, Travel accommodations, Flatiron—Consultant, Ipsen—Honorarium, Janssen Pharmaceuticals—Research, Consultant, Independent Data Monitoring Committee (IDMC), Leidos Biomedical Research—Consultant, Merck Sharp & Dohme—Consultant, Michael J Hennessey Associates – Honorarium, Consultant, Millennium Medical Publishing, Clinical Advances in Hematology & Oncology—Co-Editor-in-Chief, Modra Pharmaceuticals—Advisory Board, Myovant Sciences, Inc—Consultant, Nektar Therapeutics—Steering Committee, Novartis—Research, Physician Education Resource LLC—Consultant, Pfizer—Research, Consultant, Steering Committee, Honorarium, Sanofi—Research, Consultant, Speaker, Honorarium, Travel accommodations, UroGPO—Honorarium, UroToday—Honorarium, Travel accommodations, Vizuri Health Sciences, LLC—Consultant, NCI—Steering Committee. AJA: consultant and/or advisor for AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Merck & Co; Pfizer, EMD Serono. Paid DSMB member: Eisai. Grant/Research Support from AstraZeneca; Bristol-Myers Squibb and Merck & Co. Other financial or material support from Arcus Biosciences; Astellas Pharma US; Celgene Corporation; Clovis Oncology; Pfizer; Prometheus Biosciences and Seattle Genetics in the form of research support to institution. EA: grants and personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Astellas, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, grants and personal fees from Dendreon, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Invitae, grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants and personal fees from Clovis, grants and personal fees from Merck, grants from Johnson & Johnson, grants from Genentech, grants from Novartis, grants from Bristol Myers-Squibb; and a patent (PCT/US2015/046806; US20170275673A1) on an AR-V7 biomarker technology that is licensed to Qiagen. AJA: consulting fees: AstraZeneca, Merck, Dendreon, Janssen, Clovis, Bayer and Medivation/Astellas; speaking fees: Bayer and Dendreon, Research funding to Duke: Janssen, Medivation/Astellas, Sanofi-Aventis, Active Biotech, Bayer, Dendreon, Merck, AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Constellation, Novartis and Pfizer.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
