Machine learning active-nematic hydrodynamics
- PMID: 33653956
- PMCID: PMC7958379
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016708118
Machine learning active-nematic hydrodynamics
Erratum in
-
Correction for Colen et al., Machine learning active-nematic hydrodynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2502090122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2502090122. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40096619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
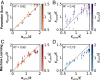
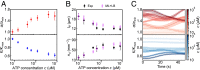
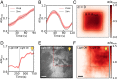
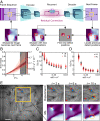
Hydrodynamic theories effectively describe many-body systems out of equilibrium in terms of a few macroscopic parameters. However, such parameters are difficult to determine from microscopic information. Seldom is this challenge more apparent than in active matter, where the hydrodynamic parameters are in fact fields that encode the distribution of energy-injecting microscopic components. Here, we use active nematics to demonstrate that neural networks can map out the spatiotemporal variation of multiple hydrodynamic parameters and forecast the chaotic dynamics of these systems. We analyze biofilament/molecular-motor experiments with microtubule/kinesin and actin/myosin complexes as computer vision problems. Our algorithms can determine how activity and elastic moduli change as a function of space and time, as well as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or motor concentration. The only input needed is the orientation of the biofilaments and not the coupled velocity field which is harder to access in experiments. We can also forecast the evolution of these chaotic many-body systems solely from image sequences of their past using a combination of autoencoders and recurrent neural networks with residual architecture. In realistic experimental setups for which the initial conditions are not perfectly known, our physics-inspired machine-learning algorithms can surpass deterministic simulations. Our study paves the way for artificial-intelligence characterization and control of coupled chaotic fields in diverse physical and biological systems, even in the absence of knowledge of the underlying dynamics.
Keywords: active turbulence; biomaterials; deep learning; liquid crystals; topological defects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Learning active nematics one step at a time.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 23;118(12):e2102169118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2102169118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33707217 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Carleo G., et al. , Machine learning and the physical sciences. Rev. Mod. Phys. 91, 45002 (2019).
-
- Lecun Y., Bengio Y., Hinton G., Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Schmidhuber J., Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Network. 61, 85–117 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Schoenholz S., Cubuk E., Sussman D., Kaxiras E., Liu A., A structural approach to relaxation in glassy liquids. Nat. Phys. 12, 469–471 (2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

