Ivermectin converts cold tumors hot and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade for treatment of breast cancer
- PMID: 33654071
- PMCID: PMC7925581
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-021-00229-5
Ivermectin converts cold tumors hot and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade for treatment of breast cancer
Abstract
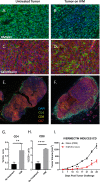
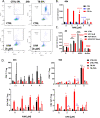
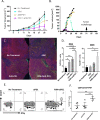
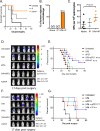
We show that treatment with the FDA-approved anti-parasitic drug ivermectin induces immunogenic cancer cell death (ICD) and robust T cell infiltration into breast tumors. As an allosteric modulator of the ATP/P2X4/P2X7 axis which operates in both cancer and immune cells, ivermectin also selectively targets immunosuppressive populations including myeloid cells and Tregs, resulting in enhanced Teff/Tregs ratio. While neither agent alone showed efficacy in vivo, combination therapy with ivermectin and checkpoint inhibitor anti-PD1 antibody achieved synergy in limiting tumor growth (p = 0.03) and promoted complete responses (p < 0.01), also leading to immunity against contralateral re-challenge with demonstrated anti-tumor immune responses. Going beyond primary tumors, this combination achieved significant reduction in relapse after neoadjuvant (p = 0.03) and adjuvant treatment (p < 0.001), and potential cures in metastatic disease (p < 0.001). Statistical modeling confirmed bona fide synergistic activity in both the adjuvant (p = 0.007) and metastatic settings (p < 0.001). Ivermectin has dual immunomodulatory and ICD-inducing effects in breast cancer, converting cold tumors hot, thus represents a rational mechanistic partner with checkpoint blockade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Disis, M. L. & Stanton, S. E. Triple-negative breast cancer: immune modulation as the new treatment paradigm. in American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Meeting, e25–e30 (American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2015). - PubMed
-
- Cortés J, et al. LBA21 - KEYNOTE-119: phase III study of pembrolizumab (pembro) versus single-agent chemotherapy (chemo) for metastatic triple negative breast cancer (mTNBC) Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:v859–v860. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz394.010. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

