Convallatoxin Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization to Attenuate Atherosclerosis Through PPARγ-Integrin αvβ5 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33654384
- PMCID: PMC7914072
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S288728
Convallatoxin Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization to Attenuate Atherosclerosis Through PPARγ-Integrin αvβ5 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
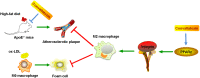
Introduction: As the primary immune cells, macrophages play a key role in atherosclerotic progression. M2 macrophage polarization has been reported to promote tissue repair and attenuate plaque formation upon the expression of anti-inflammatory factors. Convallatoxin (CNT) is a natural cardiac glycoside with anti-inflammatory pharmacological properties. However, whether CNT protects against atherosclerosis (AS) and underlying mechanisms is unknown. This work was designed to explore the potential effects of CNT on atherosclerosis.
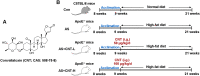
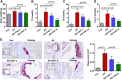
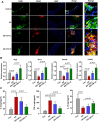
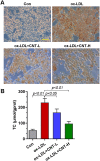
Methods: In this study, Apolipoprotein E deficiency (ApoE-/-) mice fed with high-fat diet were established, and CNT (50 or 100 μg/kg) were intragastrically administrated for 12 weeks every day. In vitro, RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with ox-LDL were treated with CNT (50 or 100 nM) for 24 h. The specific PPARγ antagonist, GW9662, was used to block the PPARγ signaling pathway in vitro. Then, the atherosclerotic lesions, macrophage polarization markers, inflammatory cytokines and PPARγ signaling pathway were examined in further examinations.
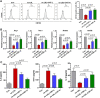
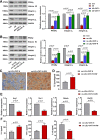
Results: Our results showed that the atherosclerotic lesions were reduced by CNT, as demonstrated by the downregulation of serum lipid level and aortic plaque area in AS mice. Furthermore, we found that CNT treatment promoted the expression of M2 macrophage markers (Arg1, Mrc1, Retnla and Chi3l3), and decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α), accompanied by the increase of anti-inflammatory factor (IL-10) in aortic vessels of AS mice. In ox-LDL-induced RAW264.7 cells, CNT administration also facilitated macrophages polarizing towards M2 subtype and inhibited inflammatory responses. Furthermore, both the in vivo and in vitro experiments showed CNT could increase the expression of PPARγ, Integrin αv and Integrin β5, and GW9662 could block CNT-induced M2 macrophage polarization.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that CNT may promote M2 macrophage polarization to exert an anti-atherosclerotic effect, partially through activating PPARγ-Integrin αvβ5 signaling pathway.
Keywords: PPARγ-Integrin αvβ5 signaling pathway; atherosclerosis; convallatoxin; macrophage polarization; ox-LDL.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) induces the gene expression of integrin αVβ5 to promote macrophage M2 polarization.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 26;293(43):16572-16582. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003161. Epub 2018 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30181212 Free PMC article.
-
[Zhuyu Pills promote polarization of macrophages toward M2 phenotype to prevent atherosclerosis via PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jan;49(1):243-250. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230823.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38403357 Chinese.
-
Pseudolaric acid B attenuates atherosclerosis progression and inflammation by suppressing PPARγ-mediated NF-κB activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Jun;59:76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.041. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29631101
-
Role of prostaglandin E2 in macrophage polarization: Insights into atherosclerosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jan;207:115357. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115357. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36455672 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Diseases.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2023;16(1):2-14. doi: 10.2174/1874467215666220324114624. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35331128 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Integrin in Cardiovascular Diseases: From Basic Research to Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 7;25(7):4096. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074096. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Macrophages in Atherosclerosis: Participants and Therapists.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025 Apr;39(2):459-472. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07513-5. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025. PMID: 37864633 Review.
-
The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma and Atherosclerosis: Post-translational Modification and Selective Modulators.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 2;13:826811. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.826811. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35309069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Macrophages in Atherogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:785220. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.785220. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin Equipped Nanozyme-Like Metal-Organic Framework Platform for the Targeted Atherosclerosis Treatment with Lipid Regulation and Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Capability.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jul;11(26):e2309062. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309062. Epub 2024 May 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38696653 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

