CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing of Plasmodium knowlesi
- PMID: 33654746
- PMCID: PMC7842605
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3522
CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing of Plasmodium knowlesi
Abstract
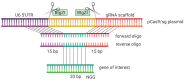
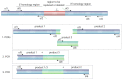
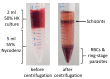
Plasmodium knowlesi is a zoonotic malaria parasite in Southeast Asia that can cause severe and fatal malaria in humans. The main hosts are Macaques, but modern diagnostic tools reveal increasing numbers of human infections. After P. falciparum, P. knowlesi is the only other malaria parasite capable of being maintained in long term in vitro culture with human red blood cells (RBCs). Its closer ancestry to other non-falciparum human malaria parasites, more balanced AT-content, larger merozoites and higher transfection efficiencies, gives P. knowlesi some key advantages over P. falciparum for the study of malaria parasite cell/molecular biology. Here, we describe the generation of marker-free CRISPR gene-edited P. knowlesi parasites, the fast and scalable production of transfection constructs and analysis of transfection efficiencies. Our protocol allows rapid, reliable and unlimited rounds of genome editing in P. knowlesi requiring only a single recyclable selection marker.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Genome editing; Malaria; Orthologue replacement; Plasmodium knowlesi; Plasmodium vivax; Transfection.
Copyright © The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Cooper D. J., Rajahram G. S., William T., Jelip J., Mohammad R., Benedict J., Alaza D. A., Malacova E., Yeo T. W., Grigg M. J., Anstey N. M. and Barber B. E.(2020). Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in Sabah, Malaysia, 2015-2017: ongoing increase in incidence despite near-elimination of the human-only Plasmodium species . Clin Infect Dis 70(3):361-367. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ecker A., Moon R., Sinden R. E. and Billker O.(2006). Generation of gene targeting constructs for Plasmodium berghei by a PCR-based method amenable to high throughput applications . Mol Biochem Parasitol 145(2): 265-268. - PubMed
-
- Ghorbal M., Gorman M., Macpherson C. R., Martins R. M., Scherf A. and Lopez-Rubio J. J.(2014). Genome editing in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using the CRISPR-Cas9 system . Nat Biotechnol 32(8): 819-821. - PubMed
-
- Knuepfer E., Wright K. E., Prajapati S. K., Rawlinson T. A., Mohring F., Koch M., Lyth O. R., Howell S. A., Villasis E., Snijders A. P., Moon R. W., Draper S. J., Rosanas-Urgell A., Higgins M. K., Baum J. and Holder A. A.(2019). Divergent roles for the RH5 complex components, CyRPA and RIPR in human-infective malaria parasites. Plos Pathog 15(6). - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

