Detachment Procedure of Bacteria from Atmospheric Particles for Flow-cytometry Counting
- PMID: 33654791
- PMCID: PMC7854139
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3273
Detachment Procedure of Bacteria from Atmospheric Particles for Flow-cytometry Counting
Abstract
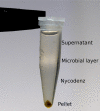
The protocol separates bacteria from atmospheric particles, obtaining with greater precision their abundance in the atmospheric deposition. This procedure is similar to the one used to separate bacteria in streambed sediments. The detachment procedure consists of a chemical treatment with sodium pyrophosphate and Tween 20 and a physical treatment with agitation and ultrasonic bath to disperse the bacteria in the liquid sample. We recover the total (free and attached) bacteria by generating a density gradient with Nycodenz by centrifugation. The techniques prior to this procedure do not include the microorganisms that are attached to the aerosol particles and, therefore, considerably underestimate the total load and deposition of airborne microorganisms.
Keywords: Airborne bacteria; Bioaerosol; Cloud condensation nuclei; Ice condensation nuclei; Microbial dispersal.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Aller J. Y., Kuznetsova M. R., Jahns C. J. and Kemp P. F.(2005). The sea surface microlayer as a source of viral and bacterial enrichment in marine aerosols. J Aerosol Sci 36(5-6): 801-812.
-
- Amalfitano S. and Fazi S.(2008). Recovery and quantification of bacterial cells associated with streambed sediments. J Microbiol Methods 75(2): 237-243. - PubMed
-
- Creamean J. M., Suski K. J., Rosenfeld D., Cazorla A., DeMott P. J., Sullivan R. C., White A. B., Ralph F. M., Minnis P., Comstock J. M., Tomlinson J. M. and Prather K. A.(2013). Dust and biological aerosols from the Sahara and Asia influence precipitation in the western U.S. Science 339(6127): 1572-1578. - PubMed
-
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky J., Kampf C. J., Weber B., Huffman J. A., Pöhlker C., Andreae M. O., Lang-Yona N., Burrows S. M., Gunthe S. S., Elbert W., Su H., Hoor P., Thines E., Hoffmann T., Després V. R. and Pöschla U.(2016). Bioaerosols in the Earth system: Climate, health, and ecosystem interactions. Atmos Res 182: 346-376.
-
- Gasol J. M., and Del Giorgio P. A.(2000). Using flow cytometry for counting natural planktonic bacteria and understanding the structure of planktonic bacterial communities. Sci Mar 64(2): 197-224.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

