Simple Protocol for Distinguishing Drug-induced Effects on Spatial Memory Acquisition, Consolidation and Retrieval in Mice Using the Morris Water Maze
- PMID: 33654872
- PMCID: PMC7854118
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3376
Simple Protocol for Distinguishing Drug-induced Effects on Spatial Memory Acquisition, Consolidation and Retrieval in Mice Using the Morris Water Maze
Abstract
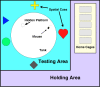
The Morris water maze (MWM) is one of the most commonly used tests for assessing spatial learning and memory in mice. While the MWM is highly amenable to testing the effects of memory modifying drugs, most studies do not consider the timing or duration of drug exposure when conducting the MWM assay; factors that can strongly influence the effect of the drug on different stages of memory and interfere with data interpretation. Herein we describe a MWM protocol which offers the advantage of distinguishing the impact of a fast acting intraperitoneally (IP) injected drug on the different stages of spatial memory: acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval. Mice initially undergo habituation to both the MWM apparatus and IP injection procedure over the course of three days. For assessing the effect of a drug on memory acquisition, mice are injected with the drug prior to training sessions over four consecutive days, where mice learn to find an escape platform in a circular water tank using distal spatial cues. To determine the effect of the drug on memory consolidation, mice are injected with the drug immediately after each training session. For testing the effect of a drug on memory retrieval, mice receive mock IP injections on each training day and the drug is IP injected only once, prior to a probe trial, where mice attempt to locate the platform following its removal from the tank. This protocol provides a simple strategy for distinguishing the effect(s) of a CNS acting drug on the different stages of memory.
Keywords: ANY-Maze; Drug intervention; Fast acting drug; Intraperitoneal injection; Learning; Morris water maze; Simplified method; Spatial memory.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abel T. and Lattal K. M.(2001). Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11(2): 180-187. - PubMed
-
- Bonini J. S., Da Silva W. C., Bevilaqua L. R., Medina J. H., Izquierdo I. and Cammarota M.(2007). On the participation of hippocampal PKC in acquisition, consolidation and reconsolidation of spatial memory. Neuroscience 147(1): 37-45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

