Anisotropic effect of a magnetic field on the neutron spin resonance in FeSe
- PMID: 33655092
- PMCID: PMC7918269
- DOI: 10.1103/physrevb.101.140504
Anisotropic effect of a magnetic field on the neutron spin resonance in FeSe
Abstract
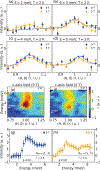
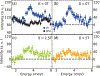
We use inelastic neutron scattering to study the effect of a magnetic field on the neutron spin resonance (E r = 3.6 meV) of superconducting FeSe (T c = 9 K). While a field aligned along the in-plane direction broadens and suppresses the resonance, a c-axis aligned field does so much more efficiently, consistent with the anisotropic field-induced suppression of the superfluid density from the heat capacity measurements. These results suggest that the resonance in FeSe is associated with the superconducting electrons arising from orbital selective quasiparticle excitations between the hole and electron Fermi surfaces.
Figures


References
-
- Bardeen J, Cooper LN, and Schrieffer JR, Microscopic theory of superconductivity, Phys. Rev 106, 162 (1957).
-
- Norman MR, The challenge of unconventional superconductivity, Science 332, 196–200 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Keimer B, Kivelson SA, Norman MR, Uchida S, and Zaanen J, From quantum matter to high-temperature superconductivity in copper oxides, Nature (London) 518, 179 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Scalapino DJ, A common thread: The pairing interaction for unconventional superconductors, Rev. Mod. Phys 84, 1383 (2012).
-
- Eschrig M, The effect of collective spin-1 excitations on electronic spectra in high-Tc superconductors, Adv. Phys 55, 47 (2006).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
