This is a preprint.
The proximal proteome of 17 SARS-CoV-2 proteins links to disrupted antiviral signaling and host translation
- PMID: 33655243
- PMCID: PMC7924263
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.02.23.432450
The proximal proteome of 17 SARS-CoV-2 proteins links to disrupted antiviral signaling and host translation
Update in
-
The proximal proteome of 17 SARS-CoV-2 proteins links to disrupted antiviral signaling and host translation.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Oct 1;17(10):e1009412. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009412. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34597346 Free PMC article.
Abstract
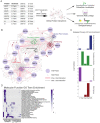
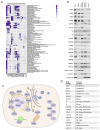
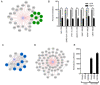
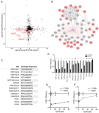
Viral proteins localize within subcellular compartments to subvert host machinery and promote pathogenesis. To study SARS-CoV-2 biology, we generated an atlas of 2422 human proteins vicinal to 17 SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins using proximity proteomics. This identified viral proteins at specific intracellular locations, such as association of accessary proteins with intracellular membranes, and projected SARS-CoV-2 impacts on innate immune signaling, ER-Golgi transport, and protein translation. It identified viral protein adjacency to specific host proteins whose regulatory variants are linked to COVID-19 severity, including the TRIM4 interferon signaling regulator which was found proximal to the SARS-CoV-2 M protein. Viral NSP1 protein adjacency to the EIF3 complex was associated with inhibited host protein translation whereas ORF6 localization with MAVS was associated with inhibited RIG-I 2CARD-mediated IFNB1 promoter activation. Quantitative proteomics identified candidate host targets for the NSP5 protease, with specific functional cleavage sequences in host proteins CWC22 and FANCD2. This data resource identifies host factors proximal to viral proteins in living human cells and nominates pathogenic mechanisms employed by SARS-CoV-2.
Author summary: SARS-CoV-2 is the latest pathogenic coronavirus to emerge as a public health threat. We create a database of proximal host proteins to 17 SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins. We validate that NSP1 is proximal to the EIF3 translation initiation complex and is a potent inhibitor of translation. We also identify ORF6 antagonism of RNA-mediate innate immune signaling. We produce a database of potential host targets of the viral protease NSP5, and create a fluorescence-based assay to screen cleavage of peptide sequences. We believe that this data will be useful for identifying roles for many of the uncharacterized SARS-CoV-2 proteins and provide insights into the pathogenicity of new or emerging coronaviruses.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(20):1953–66. - PubMed
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1814–20. - PubMed
-
- Rigaut G, Shevchenko A, Rutz B, Wilm M, Mann M, Seraphin B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17(10):1030–2. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
