This is a preprint.
Initial evaluation of a mobile SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP testing strategy
- PMID: 33655260
- PMCID: PMC7924282
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.07.28.20164038
Initial evaluation of a mobile SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP testing strategy
Update in
-
Initial Evaluation of a Mobile SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP Testing Strategy.J Biomol Tech. 2021 Sep;32(3):137-147. doi: 10.7171/jbt.21-32-03-009. J Biomol Tech. 2021. PMID: 35035293 Free PMC article.
Abstract
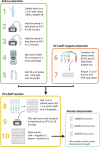
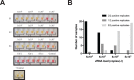
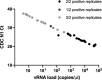
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) control in the United States remains hampered, in part, by testing limitations. We evaluated a simple, outdoor, mobile, colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay workflow where self-collected saliva is tested for SARS-CoV-2 RNA. From July 16 to November 19, 2020, 4,704 surveillance samples were collected from volunteers and tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 5 sites. A total of 21 samples tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-LAMP; 12 were confirmed positive by subsequent quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) testing, while 8 were negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, and 1 could not be confirmed because the donor did not consent to further molecular testing. We estimated the RT-LAMP assay's false-negative rate from July 16 to September 17, 2020 by pooling residual heat-inactivated saliva that was unambiguously negative by RT-LAMP into groups of 6 or less and testing for SARS-CoV-2 RNA by qRT-PCR. We observed a 98.8% concordance between the RT-LAMP and qRT-PCR assays, with only 5 of 421 RT-LAMP negative pools (2,493 samples) testing positive in the more sensitive qRT-PCR assay. Overall, we demonstrate a rapid testing method that can be implemented outside the traditional laboratory setting by individuals with basic molecular biology skills and can effectively identify asymptomatic individuals who would not typically meet the criteria for symptom-based testing modalities.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: C.M.N., D.M.D, A.M.W., D.H.O., and T.C.F. provided consulting services to Salus Discovery LLC. D.H.O. is also a consultant for Batelle.
Figures
References
-
- Havers FP, Reed C, Lim T, Montgomery JM, Klena JD, Hall AJ, Fry AM, Cannon DL, Chiang CF, Gibbons A, Krapiunaya I, Morales-Betoulle M, Roguski K, Rasheed MAU, Freeman B, Lester S, Mills L, Carroll DS, Owen SM, Johnson JA, Semenova V, Blackmore C, Blog D, Chai SJ, Dunn A, Hand J, Jain S, Lindquist S, Lynfield R, Pritchard S, Sokol T, Sosa L, Turabelidze G, Watkins SM, Wiesman J, Williams RW, Yendell S, Schiffer J, Thornburg NJ. Seroprevalence of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in 10 Sites in the United States, March 23-May 12, 2020. JAMA Intern Med 2020, 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.4130 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arons MM, Hatfield KM, Reddy SC, Kimball A, James A, Jacobs JR, Taylor J, Spicer K, Bardossy AC, Oakley LP, Tanwar S, Dyal JW, Harney J, Chisty Z, Bell JM, Methner M, Paul P, Carlson CM, McLaughlin HP, Thornburg N, Tong S, Tamin A, Tao Y, Uehara A, Harcourt J, Clark S, Brostrom-Smith C, Page LC, Kay M, Lewis J, Montgomery P, Stone ND, Clark TA, Honein MA, Duchin JS, Jernigan JA. Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Transmission in a Skilled Nursing Facility. N Engl J Med 2020, 382:2081–2090. 10.1056/NEJMoa2008457 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
