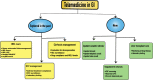
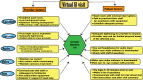
Successful Distancing: Telemedicine in Gastroenterology and Hepatology During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33655456
- PMCID: PMC7925138
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-021-06874-x
Successful Distancing: Telemedicine in Gastroenterology and Hepatology During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Telemedicine involves delivering healthcare and preventative care services to patients without the need for in-person encounters. Traditionally, telemedicine has been used for acute events (e.g., stroke, used to relay essential information to the emergency department) and chronic disease management (e.g., diabetes and chronic kidney disease management). Though the utilization of telemedicine in gastroenterology and hepatology has been modest at best, especially for inflammatory bowel diseases and chronic liver disease management, since the onset of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, utilization of telemedicine in gastroenterology increased by 4000% in the first two weeks, equivalent to the last six years of growth before the pandemic. The Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) relaxed rules for the use of telemedicine with easing restrictions on reimbursements, location, licensing requirements (across state lines), and the need for a prior provider-patient relationship. These changes increased the use of telemedicine in inpatient and outpatient settings for gastroenterology-related referrals. The use of inpatient telephonic or video consults helps provide timely care during the pandemic while conserving personal protective equipment and decreasing provider and patient exposure. Nevertheless, telehealth use comes at the cost of no direct patient contact and lesser reimbursements. The appropriate use of technology and equipment, training of healthcare providers, use of platforms that can be integrated into the electronic health record while protecting the privacy and the flow of information are essential components of telemedicine. Furthermore, encouraging patients to seek medical care remotely with the proper equipment and improving digital literacy without the need for physical examinations is a challenge, further compounded in elderly or hard-of-hearing patients and in patients who are more comfortable with in-person visits. The authors will systematically review and discuss how telemedicine can be integrated into the practice of gastroenterology and hepatology, with emphasis placed on discussing barriers to success and the ways they can be mitigated.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Gastroenterology; Hepatology; IBD; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2; Telehealth; Telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Hemant Goyal owns stock of Conversion Labs, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Evaluating IBD Patient-Initiated Electronic Communication During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: A Single-Center Study.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Jul;66(7):2468-2469. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06977-5. Epub 2021 May 21. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34021426 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Correct use of telemedicine in gastroenterology, hepatology, and endoscopy during and after the COVID-19 pandemic: Recommendations from the Italian association of hospital gastroenterologists and endoscopists (AIGO).Dig Liver Dis. 2021 Oct;53(10):1221-1227. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.06.032. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 34312103
-
Reflecting on Plastic Surgery Training During Early COVID-19 Pandemic: Resident Exposure and Telemedicine.J Craniofac Surg. 2022 Sep 1;33(6):1820-1824. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000008471. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Craniofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35762598 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatology in the Digital Era: A Review of Telehealth Care for Liver Disease.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025 Mar 28;27(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s11894-025-00972-w. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40153166 Review.
-
Telemedicine in Hepatology: Current Applications and Future Directions.Liver Transpl. 2022 Feb;28(2):294-303. doi: 10.1002/lt.26293. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Liver Transpl. 2022. PMID: 34506686 Review.
-
International Organization for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Global Strategies for Telemedicine and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.J Crohns Colitis. 2020 Oct 21;14(14 Suppl 3):S780-S784. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa140. J Crohns Colitis. 2020. PMID: 33085971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 in gastroenterology: Where are we now? Current evidence on the impact of COVID-19 in gastroenterology.United European Gastroenterol J. 2021 Sep;9(7):750-765. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12115. Epub 2021 Jun 30. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021. PMID: 34190413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterprise-led internet healthcare provision in China: insights from a leading platform.Front Digit Health. 2025 Mar 3;7:1491183. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1491183. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40099033 Free PMC article.
-
Transition to Virtual Asthma Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Observational Study.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Jun;10(6):1569-1576. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.02.027. Epub 2022 Mar 6. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35263682 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients' Perspectives during COVID-19 Pandemic: Results from a Portuguese Survey.GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2021 Sep 16;5(5):1-9. doi: 10.1159/000518945. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34934777 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Prediction Model for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Based on Laboratory Markers. Working Model in a Discovery Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 16;10(20):4745. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204745. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. TELEMEDICINE Opportunities and developments in Member States. Global Observatory for eHealth series - Volume 2. 2010. https://www.who.int/goe/publications/goe_telemedicine_2010.pdf. Accessed December 16 2020.
-
- Gutovitz S, Leggett J, Hart L, Leaman SM, James H, Stillinger T. The impact of tele-neurologists on acute stroke care at an advanced primary stroke centre. J Telemed Telecare. 2020;13:1357633X20921039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous