Targeting the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2: From the Establishment of High Throughput Screening to the Design of Tailored Inhibitors
- PMID: 33655614
- PMCID: PMC8014119
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202016961
Targeting the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2: From the Establishment of High Throughput Screening to the Design of Tailored Inhibitors
Abstract
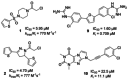
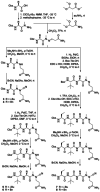
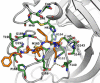
The main protease of SARS-CoV-2 (Mpro ), the causative agent of COVID-19, constitutes a significant drug target. A new fluorogenic substrate was kinetically compared to an internally quenched fluorescent peptide and shown to be ideally suitable for high throughput screening with recombinantly expressed Mpro . Two classes of protease inhibitors, azanitriles and pyridyl esters, were identified, optimized and subjected to in-depth biochemical characterization. Tailored peptides equipped with the unique azanitrile warhead exhibited concomitant inhibition of Mpro and cathepsin L, a protease relevant for viral cell entry. Pyridyl indole esters were analyzed by a positional scanning. Our focused approach towards Mpro inhibitors proved to be superior to virtual screening. With two irreversible inhibitors, azanitrile 8 (kinac /Ki =37 500 m-1 s-1 , Ki =24.0 nm) and pyridyl ester 17 (kinac /Ki =29 100 m-1 s-1 , Ki =10.0 nm), promising drug candidates for further development have been discovered.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 main protease; azapeptide nitriles; fluorogenic substrates; high throughput screening; pyridinyl 1H-indole-carboxylates.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- None
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

