Emotional eating across different eating disorders and the role of body mass, restriction, and binge eating
- PMID: 33656204
- PMCID: PMC8252459
- DOI: 10.1002/eat.23477
Emotional eating across different eating disorders and the role of body mass, restriction, and binge eating
Abstract
Objective: Different subtypes of eating disorders (ED) show dysfunctional eating behaviors such as overeating and/or restriction in response to emotions. Yet, systematic comparisons of all major EDs on emotional eating patterns are lacking. Furthermore, emotional eating correlates with body mass index (BMI), which also differs between EDs and thus confounds this comparison.
Method: Interview-diagnosed female ED patients (n = 204) with restrictive (AN-R) or binge-purge anorexia nervosa (AN-BP), bulimia nervosa (BN), or binge-eating disorder (BED) completed a questionnaire assessing "negative emotional eating" (sadness, anger, anxiety) and "happiness eating." ED groups were compared to BMI-matched healthy controls (HCs; n = 172 ranging from underweight to obesity) to exclude BMI as a confound.
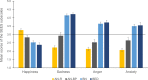
Results: Within HCs, higher BMI was associated with higher negative emotional eating and lower happiness eating. AN-R reported the lowest degree of negative emotional eating relative to other EDs and BMI-matched HCs, and the highest degree of happiness eating relative to other EDs. The BN and BED groups showed higher negative emotional eating compared to BMI-matched HCs. Patients with AN-BP occupied an intermediate position between AN-R and BN/BED and reported less happiness eating compared to BMI-matched HCs.
Discussion: Negative emotional and happiness eating patterns differ across EDs. BMI-independent emotional eating patterns distinguish ED subgroups and might be related to the occurrence of binge eating versus restriction. Hence, different types of emotional eating can represent fruitful targets for tailored psychotherapeutic interventions. While BN and BED might be treated with similar approaches, AN-BP and AN-R would need specific treatment modules.
Keywords: anorexia nervosa; binge-eating disorder; bulimia nervosa; emotional eating; emotions; obesity; questionnaire.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Eating Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Baños, R. M. , Cebolla, A. , Moragrega, I. , Van Strien, T. , Fernández‐Aranda, F. , Agüera, Z. , … Botella, C. (2014). Relationship between eating styles and temperament in an anorexia nervosa, healthy control, and morbid obesity female sample. Appetite, 76, 76–83. 10.1016/j.appet.2014.01.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bongers, P. , Jansen, A. , Houben, K. , & Roefs, A. (2013b). Happy eating: The single target implicit association test predicts overeating after positive emotions. Eating Behaviors, 14, 348–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

