Third-generation EGFR inhibitor HS-10296 in combination with famitinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, exerts synergistic antitumor effects through enhanced inhibition of downstream signaling in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 33656275
- PMCID: PMC8046080
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13902
Third-generation EGFR inhibitor HS-10296 in combination with famitinib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, exerts synergistic antitumor effects through enhanced inhibition of downstream signaling in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
Background: As a highly heterogeneous disease, lung cancer has a multitude of cellular components and patterns of gene expression which are not dependent on a single mutation or signaling pathway. Thus, using combined drugs to treat lung cancer may be a practical strategy.
Methods: The combined antitumor effects of HS-10296, a third-generation EGFR inhibitor targeting EGFR T790M mutation, with the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) famitinib in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were evaluated by in vitro methods such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis assays, and in vivo animal efficacy studies.
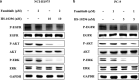
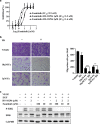
Results: Famitinib strengthened the effects of HS-10296 on inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis of NSCLC cells, possibly by synergistic inhibition of AKT and ERK phosphorylation. Meanwhile, HS-10296 significantly potentiated the effects of famitinib on inhibiting the proliferation and migration of HUVEC, which may be through synergistic inhibition of ERK phosphorylation in HUVEC, suggesting that HS-10296 may improve the inhibition of angiogenesis by famitinib. Moreover, combination of HS-10296 and famitinib exerted synergistic antitumor activity in NCI-H1975 and PC-9 xenograft models, and this effect may be accomplished by synergistic inhibition of phosphorylation of AKT and ERK and tumor angiogenesis in tumor tissues.
Conclusions: Collectively, our results indicate that HS-10296 and famitinib exhibit significant synergistic antitumor activity, suggesting that the third-generation EGFR inhibitor combined with VEGFR inhibitor provides a promising strategy in the treatment of EGFR-mutant NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer; HS-10296; famitinib; multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor; third-generation EGFR inhibitor.
© 2021 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CM082, a novel angiogenesis inhibitor, enhances the antitumor activity of gefitinib on epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1566-1577. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13430. Epub 2020 May 5. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32368855 Free PMC article.
-
The HSP90 inhibitor ganetespib potentiates the antitumor activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in mutant and wild-type non-small cell lung cancer.Target Oncol. 2015 Jun;10(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s11523-014-0329-6. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Target Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25077897 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-dependent synergistic effect of aumolertinib-pemetrexed combined therapy on EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung carcinoma with pre-clinical and clinical evidence.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 May 3;41(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02369-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35501907 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR TKI in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Oct;21(10):1287-1301. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02075-1. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30864018 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental Study of Almonertinib Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastasis and Spinal Cord Metastasis Models.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 24;12:750031. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.750031. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34630120 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab plus famitinib in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-arm, phase II trial.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Jan 1;17:17588359241311058. doi: 10.1177/17588359241311058. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39759826 Free PMC article.
-
Antineoplastic indole-containing compounds with potential VEGFR inhibitory properties.RSC Adv. 2024 Feb 14;14(9):5690-5728. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08962b. eCollection 2024 Feb 14. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38362086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2H-[1,4]oxazino-[2,3-f]quinazolin derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Feb 21. doi: 10.1039/d4md01016g. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40093516 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of PP121 in primary and metastatic non‑small cell lung cancers.Biomed Rep. 2023 Mar 1;18(4):29. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1611. eCollection 2023 Apr. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 36926188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

