Effect of Buffer on Protein Stability in Aqueous Solutions: A Simple Protein Aggregation Model
- PMID: 33656887
- PMCID: PMC8041305
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c10339
Effect of Buffer on Protein Stability in Aqueous Solutions: A Simple Protein Aggregation Model
Abstract
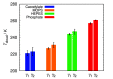
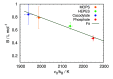
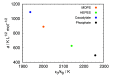
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of proteins has recently been associated with the onset of numerous diseases. Despite several studies in this area of protein aggregation, buffer-specific effects always seem to be overlooked. In this study we investigated the influence of buffers on the phase stability of hen egg-white lysozyme (HEWL) and its respective protein-protein interactions by measuring the cloud point temperature, second virial coefficient, and interaction diffusion coefficient of several HEWL-buffer solutions (MOPS, phosphate, HEPES, cacodylate) at pH 7.0. The results indicate that the buffer molecules, depending on their hydration, adsorb on the protein surface, and modulate their electrostatic stability. The obtained information was used to extend the recently developed coarse-grained protein model to incorporate buffer-specific effects. Treated by Wertheim's perturbation theory the model qualitatively correctly predicted the experimentally observed phase separation of all investigated HEWL-buffer solutions, and further allowed us to predict the phase stability of protein formulations even in experimentally unattainable conditions. Since the theory can be straightforwardly extended to include multiple components it presents a useful tool to study protein aggregation in crowded cell-like systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shin Y.; Brangwynne C. P. Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 2017, 357, 1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

