The potential for histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors as cestocidal drugs
- PMID: 33657105
- PMCID: PMC7959350
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009226
The potential for histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors as cestocidal drugs
Abstract
Background: Echinococcosis and cysticercosis are neglected tropical diseases caused by cestode parasites (family Taeniidae). Not only there is a small number of approved anthelmintics for the treatment of these cestodiases, but also some of them are not highly effective against larval stages, such that identifying novel drug targets and their associated compounds is critical. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes are validated drug targets in cancers and other diseases, and have been gaining relevance for developing new potential anti-parasitic treatments in the last years. Here, we present the anthelmintic profile for a panel of recently developed HDAC inhibitors against the model cestode Mesocestoides vogae (syn. M. corti).
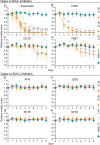
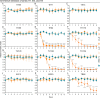
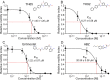
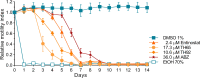
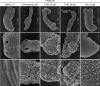
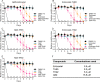
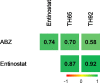
Methodology/principal findings: Phenotypic screening was performed on M. vogae by motility measurements and optical microscopic observations. Some HDAC inhibitors showed potent anthelmintic activities; three of them -entinostat, TH65, and TH92- had pronounced anthelmintic effects, reducing parasite viability by ~100% at concentrations of ≤ 20 μM. These compounds were selected for further characterization and showed anthelmintic effects in the micromolar range and in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Moreover, these compounds induced major alterations on the morphology and ultrastructural features of M. vogae. The potencies of these compounds were higher than albendazole and the anthelmintic effects were irreversible. Additionally, we evaluated pairwise drug combinations of these HDAC inhibitors and albendazole. The results suggested a positive interaction in the anthelmintic effect for individual pairs of compounds. Due to the maximum dose approved for entinostat, adjustments in the dose regime and/or combinations with currently-used anthelmintic drugs are needed, and the selectivity of TH65 and TH92 towards parasite targets should be assessed.
Conclusion, significance: The results presented here suggest that HDAC inhibitors represent novel and potent drug candidates against cestodes and pave the way to understanding the roles of HDACs in these parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of sirtuin enzymes in cestodes and evaluation of sirtuin inhibitors as new cestocidal molecules.Int J Parasitol. 2022 Apr;52(5):317-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2021.12.002. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Int J Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35150663
-
Histone deacetylase enzymes as potential drug targets of Neglected Tropical Diseases caused by cestodes.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2019 Apr;9:120-132. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30897528 Free PMC article.
-
Extracts and Terpenoids from Stevia Species as Potential Anthelmintics for Neglected Tropical Diseases Caused by Cestode Parasites.Molecules. 2024 Sep 18;29(18):4430. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184430. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339424 Free PMC article.
-
Entinostat (SNDX-275) for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(8):1101-9. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2015.1056779. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26098363 Review.
-
A perspective on the discovery of selected compounds with anthelmintic activity against the barber's pole worm-Where to from here?Adv Parasitol. 2020;108:1-45. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2019.12.003. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Adv Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32291083 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in non-neoplastic diseases.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 2;10(13):e33997. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33997. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Schistosomiasis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 10;15(1):80. doi: 10.3390/ph15010080. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase 2 and 3 of Sarcoptes scabiei: characterization of a potential drug target.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 22;12(12):e0073724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00737-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39436071 Free PMC article.
-
How to Slow down the Ticking Clock: Age-Associated Epigenetic Alterations and Related Interventions to Extend Life Span.Cells. 2022 Jan 29;11(3):468. doi: 10.3390/cells11030468. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Albendazole specifically disrupts microtubules and protein turnover in the tegument of the cestode Mesocestoides corti.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 4;21(6):e1013221. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013221. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40465816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Accelerating Work To Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: a roadmap for implementation: executive summary. Geneva: World Heal Organ. 2012:15. doi: WHO/HTM/NTD/2012.1
-
- Kyung SY, Cho YK, Kim YJ, Park J-W, Jeong SH, Lee J-I, et al.. A Paragonimiasis Patient with Allergic Reaction to Praziquantel and Resistance to Triclabendazole: Successful Treatment after Desensitization to Praziquantel. Korean J Parasitol. 2011. 49: 73. 10.3347/kjp.2011.49.1.73 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

