Long-term platelet priming after glycoprotein VI stimulation in comparison to Protease-Activating Receptor (PAR) stimulation
- PMID: 33657162
- PMCID: PMC7928515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247425
Long-term platelet priming after glycoprotein VI stimulation in comparison to Protease-Activating Receptor (PAR) stimulation
Abstract
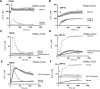
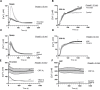
Platelets can respond to multiple antagonists and agonists, implying that their activation state is a consequence of past exposure to these substances. While platelets are often considered as one-time responsive cells, they likely can respond to sequential application of inhibitors and stimuli. We hypothesized that the ability of platelets to sequentially respond depends on the time and type of repeated agonist application. The present proof-of-concept data show that iloprost (cAMP elevation), tirofiban (integrin αIIbβ3 blocker) and Syk kinase inhibition subacutely modulated platelet aggregation, i.e. halted this process even when applied after agonist. In comparison to thrombin-activated receptor (PAR) stimulation, glycoprotein VI (GPVI) stimulation was less sensitive to time-dependent blockage of aggregation, with Syk inhibition as an exception. Furthermore, cytosolic Ca2+ measurements indicated that, when compared to PAR, prior GPVI stimulation induced a more persistent, priming activation state of platelets that influenced the response to a next agent. Overall, these data point to an unexpected priming memory of activated platelets in subacutely responding to another inhibitor or stimulus, with a higher versatility and faster offset after PAR stimulation than after GPVI stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no relevant conflicts of interest exist. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
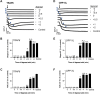
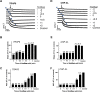
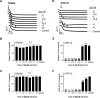
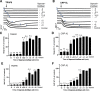
References
-
- Heemskerk JW, Vis P, Feijge MA, Hoyland J, Mason WT, Sage SO. Roles of phospholipase C and Ca2+-ATPase in calcium responses of single, fibrinogen-bound platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:356–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

