Plxdc family members are novel receptors for the rhesus monkey rhadinovirus (RRV)
- PMID: 33657166
- PMCID: PMC7959344
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008979
Plxdc family members are novel receptors for the rhesus monkey rhadinovirus (RRV)
Abstract
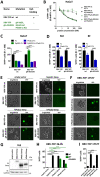
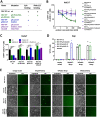
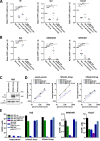
The rhesus monkey rhadinovirus (RRV), a γ2-herpesvirus of rhesus macaques, shares many biological features with the human pathogenic Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). Both viruses, as well as the more distantly related Epstein-Barr virus, engage cellular receptors from the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases (Ephs). However, the importance of the Eph interaction for RRV entry varies between cell types suggesting the existence of Eph-independent entry pathways. We therefore aimed to identify additional cellular receptors for RRV by affinity enrichment and mass spectrometry. We identified an additional receptor family, the Plexin domain containing proteins 1 and 2 (Plxdc1/2) that bind the RRV gH/gL glycoprotein complex. Preincubation of RRV with soluble Plxdc2 decoy receptor reduced infection by ~60%, while overexpression of Plxdc1 and 2 dramatically enhanced RRV susceptibility and cell-cell fusion of otherwise marginally permissive Raji cells. While the Plxdc2 interaction is conserved between two RRV strains, 26-95 and 17577, Plxdc1 specifically interacts with RRV 26-95 gH. The Plxdc interaction is mediated by a short motif at the N-terminus of RRV gH that is partially conserved between isolate 26-95 and isolate 17577, but absent in KSHV gH. Mutation of this motif abrogated the interaction with Plxdc1/2 and reduced RRV infection in a cell type-specific manner. Taken together, our findings characterize Plxdc1/2 as novel interaction partners and entry receptors for RRV and support the concept of the N-terminal domain of the gammaherpesviral gH/gL complex as a multifunctional receptor-binding domain. Further, Plxdc1/2 usage defines an important biological difference between KSHV and RRV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- O’Connor CM, Kedes DH. Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus: A Model for the Study of KSHV. In: Boshoff C, Weiss RA, editors. Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus: New Perspectives. Springer; Berlin Heidelberg; 2007. pp. 43–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

