Development of a multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) assay for on-site diagnosis of SARS CoV-2
- PMID: 33657176
- PMCID: PMC7928493
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248042
Development of a multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) assay for on-site diagnosis of SARS CoV-2
Abstract
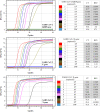
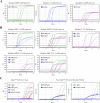
A newly identified coronavirus, designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2), has spread rapidly from its epicenter in China to more than 150 countries across six continents. In this study, we have designed three reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) primer sets to detect the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP), Envelope (E) and Nucleocapsid protein (N) genes of SARS CoV-2. For one tube reaction, the detection limits for five combination SARS CoV-2 LAMP primer sets (RdRP/E, RdRP/N, E/N, RdRP/E/N and RdRP/N/Internal control (actin beta)) were evaluated with a clinical nasopharyngeal swab sample. Among the five combination, the RdRP/E and RdRP/N/IC multiplex LAMP assays showed low detection limits. The sensitivity and specificity of the RT-LAMP assay were evaluated and compared to that of the widely used Allplex™ 2019-nCoV Assay (Seegene, Inc., Seoul, South Korea) and PowerChek™ 2019-nCoV Real-time PCR kit (Kogenebiotech, Seoul, South Korea) for 130 clinical samples from 91 SARS CoV-2 patients and 162 NP specimens from individuals with (72) and without (90) viral respiratory infections. The multiplex RdRP (FAM)/N (CY5)/IC (Hex) RT-LAMP assay showed comparable sensitivities (RdRP: 93.85%, N: 94.62% and RdRP/N: 96.92%) to that of the Allplex™ 2019-nCoV Assay (100%) and superior to those of PowerChek™ 2019-nCoV Real-time PCR kit (RdRP: 92.31%, E: 93.85% and RdRP/E: 95.38%).
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DK, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro surveillance: bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin. 2020;25(3). Epub 2020/01/30. 10.2807/1560-7917.Es.2020.25.3.2000045 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

