How I manage acquired pure red cell aplasia in adults
- PMID: 33657207
- PMCID: PMC8057257
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021010898
How I manage acquired pure red cell aplasia in adults
Abstract
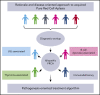
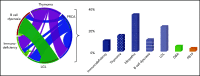
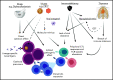
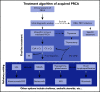
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) is a rare hematological disorder with multiple etiologies. The multifaceted nature of this disease is emphasized by the variety of concomitant clinical features. Classic idiopathic presentation aside, prompt recognition of pathogenetic clues is important because of their diagnostic and therapeutic implications. As a consequence, treatment of PRCA is diverse and strictly dependent on the presented clinical scenario. Here, we propose a series of clinical vignettes that showcase instructive representative situations derived from our routine clinical practice. Using these illustrative clinical cases, we review the diagnostic workup needed for a precise diagnosis and the currently available therapeutic options, discussing their applications in regard to the various PRCA-associated conditions and individual patients' characteristics. Finally, we propose a treatment algorithm that may offer guidance for personalized therapeutic recommendations.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Young NS, Maciejewski J. The pathophysiology of acquired aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(19):1365-1372. - PubMed
-
- Frickhofen N, Chen ZJ, Young NS, Cohen BJ, Heimpel H, Abkowitz JL. Parvovirus B19 as a cause of acquired chronic pure red cell aplasia. Br J Haematol. 1994;87(4):818-824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

