Pediatric asthma control during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 33657264
- PMCID: PMC8014816
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.418
Pediatric asthma control during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Background: The lockdown imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a completely different style of life with possible effects on the attitude toward their disease in patients with chronic lung disease, such as asthma. The aim of our study was to investigate in asthmatic children the level of asthma control and the maintenance therapy used during the lockdown.
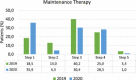
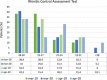
Methods: Among asthmatic children attending our clinic, we identified those who had been prescribed the same therapy in March-April 2019 and March-April 2020. The level of asthma control (GINA-score) and the maintenance therapy used during the lockdown (March-April 2020) were compared with those of March-April 2019. We separately analyzed a small group of children with severe asthma treated with Omalizumab during the lockdown.
Results: We enrolled 92 asthmatic children (67 males). Compared to 2019, in 2020 a higher proportion of children modified their maintenance therapy (38% vs. 15.2%, p < .001), with a significant increase in both the proportion of children who increased (p = .033) and in that of children who decreased their therapy (p = .026). The level of control resulted as significantly higher in 2020 (March p = .023; April p = .007). Also, the 13 children treated with Omalizumab showed a good level of control in 2020.
Conclusions: In asthmatic children, the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown had a significant impact on their asthma control and on their attitude toward maintenance therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19 lockdown; COVID-19 pandemic; asthma control; maintenance therapy; pediatric asthma.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus Emergency: The National response . Dipartimento della Protezione Civile. http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/en/risk-activities/health-risk/emerge.... Accessed August 7, 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous