Mining oomycete proteomes for metalloproteases leads to identification of candidate virulence factors in Phytophthora infestans
- PMID: 33657266
- PMCID: PMC8035641
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13043
Mining oomycete proteomes for metalloproteases leads to identification of candidate virulence factors in Phytophthora infestans
Abstract
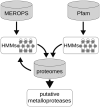
Pathogens deploy a wide range of pathogenicity factors, including a plethora of proteases, to modify host tissue or manipulate host defences. Metalloproteases (MPs) have been implicated in virulence in several animal and plant pathogens. Here we investigated the repertoire of MPs in 46 stramenopile species including 37 oomycetes, 5 diatoms, and 4 brown algae. Screening their complete proteomes using hidden Markov models (HMMs) trained for MP detection resulted in over 4,000 MPs, with most species having between 65 and 100 putative MPs. Classification in clans and families according to the MEROPS database showed a highly diverse MP repertoire in each species. Analyses of domain composition, orthologous groups, distribution, and abundance within the stramenopile lineage revealed a few oomycete-specific MPs and MPs potentially related to lifestyle. In-depth analyses of MPs in the plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans revealed 91 MPs, divided over 21 protein families, including 25 MPs with a predicted signal peptide or signal anchor. Expression profiling showed different patterns of MP gene expression during pre-infection and infection stages. When expressed in leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana, 12 MPs changed the sizes of lesions caused by inoculation with P. infestans; with 9 MPs the lesions were larger, suggesting a positive effect on the virulence of P. infestans, while 3 MPs had a negative effect, resulting in smaller lesions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic inventory of MPs in oomycetes and the first study pinpointing MPs as potential pathogenicity factors in Phytophthora.
Keywords: MEROPS; oomycete; peptidase; plant pathogen; secreted metalloproteases; stramenopile; virulence.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analyses of genome architecture and gene expression reveal novel candidate virulence factors in the secretome of Phytophthora infestans.BMC Genomics. 2010 Nov 16;11:637. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-637. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21080964 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted pectin monooxygenases drive plant infection by pathogenic oomycetes.Science. 2021 Aug 13;373(6556):774-779. doi: 10.1126/science.abj1342. Science. 2021. PMID: 34385392
-
The kinome of Phytophthora infestans reveals oomycete-specific innovations and links to other taxonomic groups.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 9;11:700. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-700. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143935 Free PMC article.
-
Phytophthora infestans small phospholipase D-like proteins elicit plant cell death and promote virulence.Mol Plant Pathol. 2019 Feb;20(2):180-193. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12746. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30171659 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic virulence determinants utilize phosphoinositides at the ER and host cell surface.Trends Microbiol. 2013 Mar;21(3):145-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.12.004. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Trends Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23375057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA silencing proteins and small RNAs in oomycete plant pathogens and biocontrol agents.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 24;14:1076522. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1076522. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37032886 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Metalloproteases in the Wheat Sharp Eyespot Pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis and a Role in Fungal Virulence.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 14;23(18):10691. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810691. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142601 Free PMC article.
-
The root pathogen Aphanomyces euteiches secretes modular proteases in pea apoplast during host infection.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 27;14:1140101. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1140101. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37051076 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane proteome analysis identifies key components of sensing in Phytophthora parasitica zoospores.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08701-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhardwaj, R. , Das, M. , Singh, S. , Chiranjivi, A.K. , Prabhu, S.V. , Singh, S.K. et al. (2017) Evaluation of CAAX prenyl protease II of Leishmania donovani as potential drug target: Infectivity and growth of the parasite is significantly lowered after the gene knockout. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 102, 156–160. - PubMed
-
- Bray, N.L. , Pimentel, H. , Melsted, P. & Pachter, L. (2016) Near‐optimal probabilistic RNA‐seq quantification. Nature Biotechnology, 34, 525–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

