Complex-dependent histone acetyltransferase activity of KAT8 determines its role in transcription and cellular homeostasis
- PMID: 33657400
- PMCID: PMC8056186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.02.012
Complex-dependent histone acetyltransferase activity of KAT8 determines its role in transcription and cellular homeostasis
Abstract
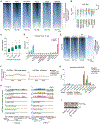
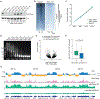
Acetylation of lysine 16 on histone H4 (H4K16ac) is catalyzed by histone acetyltransferase KAT8 and can prevent chromatin compaction in vitro. Although extensively studied in Drosophila, the functions of H4K16ac and two KAT8-containing protein complexes (NSL and MSL) are not well understood in mammals. Here, we demonstrate a surprising complex-dependent activity of KAT8: it catalyzes H4K5ac and H4K8ac as part of the NSL complex, whereas it catalyzes the bulk of H4K16ac as part of the MSL complex. Furthermore, we show that MSL complex proteins and H4K16ac are not required for cell proliferation and chromatin accessibility, whereas the NSL complex is essential for cell survival, as it stimulates transcription initiation at the promoters of housekeeping genes. In summary, we show that KAT8 switches catalytic activity and function depending on its associated proteins and that, when in the NSL complex, it catalyzes H4K5ac and H4K8ac required for the expression of essential genes.
Keywords: H4K16ac; H4K5ac; H4K8ac; KAT8; MSL complex; NSL complex; chromatin; histone acetylation; transcription.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests EpiCypher is a commercial developer and supplier of reagents (recombinant semi-synthetic modified nucleosomes) and the antibody characterization platforms used in this study. K.H. is a consultant for Inthera Bioscience AG and a scientific advisor for Hannibal Health Innovation.
Figures





References
-
- Akhtar A, and Becker PB (2000). Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 5, 367–375. - PubMed
-
- Anders S, McCarthy DJ, Chen Y, Okoniewski M, Smyth GK, Huber W, and Robinson MD (2013). Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and Bioconductor. Nat. Protoc 8, 1765–1786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

