Hallmarks of environmental insults
- PMID: 33657411
- PMCID: PMC9396710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.043
Hallmarks of environmental insults
Abstract
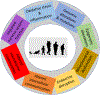
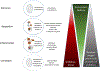
Environmental insults impair human health around the world. Contaminated air, water, soil, food, and occupational and household settings expose humans of all ages to a plethora of chemicals and environmental stressors. We propose eight hallmarks of environmental insults that jointly underpin the damaging impact of environmental exposures during the lifespan. Specifically, they include oxidative stress and inflammation, genomic alterations and mutations, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, endocrine disruption, altered intercellular communication, altered microbiome communities, and impaired nervous system function. They provide a framework to understand why complex mixtures of environmental exposures induce severe health effects even at relatively modest concentrations.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham E, Rousseaux S, Agier L, Giorgis-Allemand L, Tost J, Galineau J, Hulin A, Siroux V, Vaiman D, Charles MA, et al. (2018). Pregnancy exposure to atmospheric pollution and meteorological conditions and placental DNA methylation. Environ Int 118, 334–347. - PubMed
-
- Alkoussa S, Hulo S, Courcot D, Billet S, and Martin PJ (2020). Extracellular vesicles as actors in the air pollution related cardiopulmonary diseases. Crit Rev Toxicol 50, 402–423. - PubMed
-
- Babisch W (2011). Cardiovascular effects of noise. Noise Health 13, 201–204. - PubMed
-
- Baccarelli A, Pesatori AC, and Bertazzi PA (2000). Occupational and environmental agents as endocrine disruptors: experimental and human evidence. J Endocrinol Invest 23, 771–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

