Validation of an artificial intelligence-driven large vessel occlusion detection algorithm for acute ischemic stroke patients
- PMID: 33657922
- PMCID: PMC8559012
- DOI: 10.1177/1971400921998952
Validation of an artificial intelligence-driven large vessel occlusion detection algorithm for acute ischemic stroke patients
Abstract
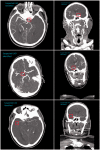
Rapid and accurate diagnosis of large vessel occlusions (LVOs) in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients using automated software could improve clinical workflow in determining thrombectomy in eligible patients. Artificial intelligence-based methods could accomplish this; however, their performance in various clinical scenarios, relative to clinical experts, must be thoroughly investigated. We aimed to assess the ability of Canon's AUTOStroke Solution LVO application in properly detecting and locating LVOs in AIS patients. Data from 202 LVO and 101 non-LVO AIS patients who presented with stroke-like symptoms between March 2019 and February 2020 were collected retrospectively. LVO patients had either an internal carotid artery (ICA) (n = 59), M1 middle cerebral artery (MCA) (n = 82) or M2 MCA (n = 61) occlusion. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans from each patient were pushed to the automation platform and analyzed. The algorithm's ability to detect LVOs was assessed using accuracy, sensitivity and Matthews correlation coefficients (MCCs) for each occlusion type. The following results were calculated for each occlusion type in the study (accuracy, sensitivity, MCC): ICA = (0.95, 0.90, 0.89), M1 MCA = (0.89, 0.77, 0.78) and M2 MCA = (0.80, 0.51, 0.59). For the non-LVO cohort, 98% (99/101) of cases were correctly predicted as LVO negative. Processing time for each case was 69.8 ± 1.1 seconds (95% confidence interval). Canon's AUTOStroke Solution LVO application was able to accurately identify ICA and M1 MCA occlusions in addition to almost perfectly assessing when an LVO was not present. M2 MCA occlusion detection needs further improvement based on the sensitivity results displayed by the LVO detection algorithm.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; CT angiography; brain; ischemic stroke.
Figures

References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018; 49: 46–99. DOI: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158.
-
- Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. New Engl J Med 2018; 378: 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Miles K, Eastwood JD, Konig M. Multidetector computed tomography in cerebrovascular disease: CT perfusion imaging. UK: CRC Press, 2007.
-
- Guenego A, Mlynash M, Christensen S, et al. Hypoperfusion ratio predicts infarct growth during transfer for thrombectomy. Ann Neurol 2018; 84: 616–620. DOI: 10.1002/ana.25320. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

