Durable memories and efficient neural coding through mnemonic training using the method of loci
- PMID: 33658191
- PMCID: PMC7929507
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc7606
Durable memories and efficient neural coding through mnemonic training using the method of loci
Abstract
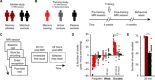
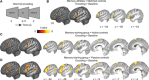
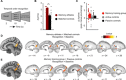
Mnemonic techniques, such as the method of loci, can powerfully boost memory. We compared memory athletes ranked among the world's top 50 in memory sports to mnemonics-naïve controls. In a second study, participants completed a 6-week memory training, working memory training, or no intervention. Behaviorally, memory training enhanced durable, longer-lasting memories. Functional magnetic resonance imaging during encoding and recognition revealed task-based activation decreases in lateral prefrontal, as well as in parahippocampal and retrosplenial cortices in both memory athletes and participants after memory training, partly associated with better performance after 4 months. This was complemented by hippocampal-neocortical coupling during consolidation, which was stronger the more durable memories participants formed. Our findings advance knowledge on how mnemonic training boosts durable memory formation through decreased task-based activation and increased consolidation thereafter. This is in line with conceptual accounts of neural efficiency and highlights a complex interplay of neural processes critical for extraordinary memory.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- F. Yates, The Art of Memory (Routledge & Kegan, 1966).
-
- J. Foer, Moonwalking with Einstein (Penguin Books, 2011).
-
- Maguire E. A., Valentine E. R., Wilding J. M., Kapur N., Routes to remembering: The brains behind superior memory. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 90–95 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

