BMPR1A maintains skeletal stem cell properties in craniofacial development and craniosynostosis
- PMID: 33658353
- PMCID: PMC8590202
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb4416
BMPR1A maintains skeletal stem cell properties in craniofacial development and craniosynostosis
Abstract
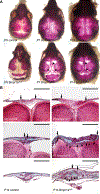
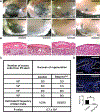
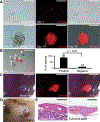
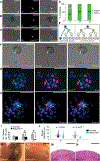
Skeletal stem cells from the suture mesenchyme, which are referred to as suture stem cells (SuSCs), exhibit long-term self-renewal, clonal expansion, and multipotency. These SuSCs reside in the suture midline and serve as the skeletal stem cell population responsible for calvarial development, homeostasis, injury repair, and regeneration. The ability of SuSCs to engraft in injury site to replace the damaged skeleton supports their potential use for stem cell-based therapy. Here, we identified BMPR1A as essential for SuSC self-renewal and SuSC-mediated bone formation. SuSC-specific disruption of Bmpr1a in mice caused precocious differentiation, leading to craniosynostosis initiated at the suture midline, which is the stem cell niche. We found that BMPR1A is a cell surface marker of human SuSCs. Using an ex vivo system, we showed that SuSCs maintained stemness properties for an extended period without losing the osteogenic ability. This study advances our knowledge base of congenital deformity and regenerative medicine mediated by skeletal stem cells.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures



References
-
- Mauffrey C, Barlow BT, Smith W, Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 23, 143–153 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F, Rouard H, Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87, 1430–1437 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Lo DD, Montoro DT, Grova M, Hyun JS, Chung MT, Wan DC, Longaker MT, Stem Cell-Based Bioengineering of Craniofacial Bone. 379–394 (2013).
-
- Panetta NJ, Gupta DM, Longaker MT, Bone regeneration and repair. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 5, 122–128 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

