Pharmacological rescue in patient iPSC and mouse models with a rare DISC1 mutation
- PMID: 33658519
- PMCID: PMC7930023
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21713-3
Pharmacological rescue in patient iPSC and mouse models with a rare DISC1 mutation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Pharmacological rescue in patient iPSC and mouse models with a rare DISC1 mutation.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 30;12(1):2570. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23263-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33931639 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
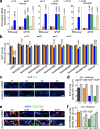
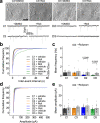
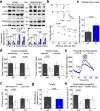
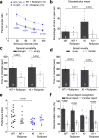
We previously identified a causal link between a rare patient mutation in DISC1 (disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1) and synaptic deficits in cortical neurons differentiated from isogenic patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Here we find that transcripts related to phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) signaling are significantly elevated in human cortical neurons differentiated from iPSCs with the DISC1 mutation and that inhibition of PDE4 or activation of the cAMP signaling pathway functionally rescues synaptic deficits. We further generated a knock-in mouse line harboring the same patient mutation in the Disc1 gene. Heterozygous Disc1 mutant mice exhibit elevated levels of PDE4s and synaptic abnormalities in the brain, and social and cognitive behavioral deficits. Pharmacological inhibition of the PDE4 signaling pathway rescues these synaptic, social and cognitive behavioral abnormalities. Our study shows that patient-derived isogenic iPSC and humanized mouse disease models are integral and complementary for translational studies with a better understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic interactions between PDE4B and GSK-3: DISC1 mutant mice.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Mar;62(3):1252-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.02.020. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 21376063
-
[11C](R)-Rolipram positron emission tomography detects DISC1 inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4 in live Disc1 locus-impaired mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Jul;39(7):1306-1313. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18758997. Epub 2018 Feb 12. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 29430995 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition enhances the dopamine D1 receptor/PKA/DARPP-32 signaling cascade in frontal cortex.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Feb;219(4):1065-79. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2436-8. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 21833500 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 and phosphodiesterase 4B: towards an understanding of psychiatric illness.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):401-5. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140210. Epub 2007 Sep 6. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17823207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia-1 (DISC1): a key susceptibility factor for major mental illnesses.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1086:126-33. doi: 10.1196/annals.1377.018. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17185511 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics of human brain development.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Jan;25(1):26-45. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00626-5. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 37507490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMDA Receptors in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Pathophysiology and Disease Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;25(22):12366. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212366. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applying stem cells and CRISPR engineering to uncover the etiology of schizophrenia.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;69:193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 May 16. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34010781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative molecular landscapes of immature neurons in the mammalian dentate gyrus across species reveal special features in humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 17:2025.02.16.638557. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.16.638557. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40027814 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Adolescent neurostimulation of dopamine circuit reverses genetic deficits in frontal cortex function.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 12:2023.02.03.526987. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.03.526987. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Oct 13;12:RP87414. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87414. PMID: 36778456 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hall J, Trent S, Thomas KL, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ. Genetic risk for schizophrenia: convergence on synaptic pathways involved in plasticity. Biol. Psychiatry. 2015;77:52–58. - PubMed
-
- Bellin M, Marchetto MC, Gage FH, Mummery CL. Induced pluripotent stem cells: the new patient? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;13:713–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

