Radioiodine labeling and in vivo trafficking of extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 33658566
- PMCID: PMC7930277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84636-5
Radioiodine labeling and in vivo trafficking of extracellular vesicles
Abstract
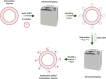
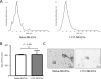
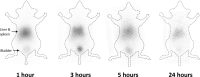
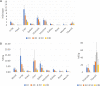
Biodistribution and role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) are still largely unknown. Reliable tracking methods for EVs are needed. In this study, nuclear imaging using radioiodine were developed and applied for tracking EVs derived from cell lines. EVs were obtained from supernatant of thyroid cancer cell (Cal62) and natural killer cells (NK92-MI) using sequential ultracentrifuges. Sulfosuccinimidyl-3-(4-hydroxypheynyl) propionate were labeled to membrane of Cal62 and NK92-MI cell derived EVs, then the EVs were labeled with radioiodine (I-131 and I-125) using pre-coated iodination tubes (RI-EVs). In vivo gamma camera images were obtained after intravenous injection of the RI-EVs, and ex vivo biodistribution study was also performed. EVs were labeled with radioiodine and radiochemical purity of the RI-EV was more than 98%. Results of nanoparticle tracking analysis and electron microscopy showed that there was no significant difference in EVs before and after the radioiodine labeling. After intravenous injection of RI-EVs to mice, gamma camera imaging well visualized the real-time biodistribution of the RI-EVs. RI-EVs were mainly visualized at liver, spleen, and lung. Nuclear imaging system of EVs derived from thyroid cancer and NK cells using radioiodine labeling of the EVs was established. Thus, this system might be helpful for in vivo tracking of EVs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
One-Minute Iodine Isotope Labeling Technology Enables Noninvasive Tracking and Quantification of Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Lesions and Intact Animals.Mol Pharm. 2023 Jul 3;20(7):3672-3682. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00299. Epub 2023 May 22. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37212215
-
A new bioluminescent reporter system to study the biodistribution of systematically injected tumor-derived bioluminescent extracellular vesicles in mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 18;8(66):109894-109914. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22493. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29299117 Free PMC article.
-
New Optical Imaging Reporter-labeled Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Platform for In Vivo Tumor Targeting in a Mouse Model.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 10;8(1):13509. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31998-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30201988 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies for labeling and tracking of extracellular vesicles.J Control Release. 2020 Dec 10;328:141-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.056. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32882270 Review.
-
Biodistribution of extracellular vesicles following administration into animals: A systematic review.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Jun;10(8):e12085. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12085. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 34194679 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unveiling Invisible Extracellular Vesicles: Cutting-Edge Technologies for Their in Vivo Visualization.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Sep-Oct;16(5):e2009. doi: 10.1002/wnan.2009. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39439198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Snorkel-tag based affinity chromatography for recombinant extracellular vesicle purification.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Oct;13(10):e12523. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12523. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 39400515 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial Probes for Nuclear Imaging.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Feb 9;12(4):582. doi: 10.3390/nano12040582. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoengineering facilitating the target mission: targeted extracellular vesicles delivery systems design.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Sep 29;20(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01638-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36175866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Standard Radio-Iodine Labeling Protocols Impaired the Functional Integrity of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Exosomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 27;25(7):3742. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073742. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thery C, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

