Lysyl oxidase engineered lipid nanovesicles for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 33658580
- PMCID: PMC7930284
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84492-3
Lysyl oxidase engineered lipid nanovesicles for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
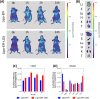
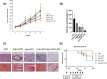
In the field of oncology research, a deeper understanding of tumor biology has shed light on the role of environmental conditions surrounding cancer cells. In this regard, targeting the tumor microenvironment has recently emerged as a new way to access this disease. In this work, a novel extracellular matrix (ECM)-targeting nanotherapeutic was engineered using a lipid-based nanoparticle chemically linked to an inhibitor of the ECM-related enzyme, lysyl oxidase 1 (LOX), that inhibits the crosslinking of elastin and collagen fibers. We demonstrated that, when the conjugated vesicles were loaded with the chemotherapeutic epirubicin, superior inhibition of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell growth was observed both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, in vivo results displayed prolonged survival, minimal cytotoxicity, and enhanced biocompatibility compared to free epirubicin and epirubicin-loaded nanoparticles. This all-in-one nano-based ECM-targeting chemotherapeutic may provide a key-enabling technology for the treatment of TNBC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

