Utility Index and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Glaucomatous Patients Comparing with Normal Participants
- PMID: 33658759
- PMCID: PMC7920622
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S300226
Utility Index and Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Glaucomatous Patients Comparing with Normal Participants
Abstract
Purpose: Utility index is a significant outcome in terms of health economics assessment while patient-reported outcome measure (PROMs) evaluates quality of life (QOL) from patient's perspective. Our objective was to evaluate both utility indices and PROMs using generic and eye specific QOL in glaucomatous patients compared with normal population.
Methods: This is a case-control study. We interviewed normal and glaucomatous participants with the European Quality of Life questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L), the European visual analogue scale (EQ-VAS) and the visual function questionnaire 28 (Thai version) (VFQ-28). The visual function questionnaire utility index (VFQ-UI) and generic utility index from EQ-5D-5L were calculated.
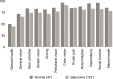
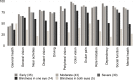
Results: There were 47 normal and 127 glaucomatous participants in this study. Amongst glaucoma group, 35 participants were in the early stage of the disease, 43 were in the moderate stage, 30 normal vision participants were in the severe stage, 14 participants had blindness one eye, and 5 had blindness both eyes. The mean age of the participants in both groups was statistically similar (63.78±6.84 vs 66.30±8.93 years old, respectively, p=0.062). Underlying diseases between groups were also comparable. The EQ-5D-5L utility index score and the EQ-VAS score were not statistically different between normal and glaucomatous groups, respectively (EQ-5D-5L: 0.874±0.122 vs 0.837±0.191, p=0.215; EQ VAS: 76.06±15.07 vs 74.02 ±15.10, p=0.43). By contrast, VFQ-UI of the glaucomatous group was significantly lower than that of the normal group, (VFQ-UI: 0.833±0.147 vs 0.895±0.070, accordingly, p<0.05).
Conclusions: Utility index from the VFQ-UI was a relevant PROMs for evaluating the QOL of glaucomatous patients in terms of visual function specificity and acceptable validity.
Keywords: EQ-5D-5L; PROMs; VFQ-28; VFQ-UI; patient-reported outcome measures; quality of life in glaucomatous patients; the European Quality of Life questionnaire in glaucoma; the visual function questionnaire 28 Thai-version; the visual function questionnaire utility index in glaucoma; utility index of glaucoma.
© 2021 Rojananuangnit and Sudjinda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Skalicky S, Goldberg I. Depression and quality of life in patients with glaucoma: a cross-sectional analysis using the geriatric depression scale-15, assessment of function related to vision, and the glaucoma quality of life-15. J Glaucoma. 2008;17(7):546–551. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e318163bdd1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources