Three-Dimensional Ex Vivo Culture for Drug Responses of Patient-Derived Gastric Cancer Tissue
- PMID: 33659211
- PMCID: PMC7917258
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.614096
Three-Dimensional Ex Vivo Culture for Drug Responses of Patient-Derived Gastric Cancer Tissue
Abstract
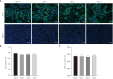
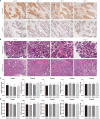
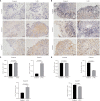
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common malignancies with high mortality and substantial morbidity. Although the traditional treatment strategies for GC revolve around surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy, none have been able to optimally treat most affected patients. To improve clinical outcomes and overcome potential GC resistance, we established a three-dimensional (3D) culturing platform that accurately predicts drug responses in a time- and cost-effective manner. We collected tumor tissues from patients following surgeries and cultured them for 3 days using our protocol. We first evaluated cell proliferation, viability, and apoptosis using the following markers: Ki67 and cleaved caspase 3 (Cas3). We demonstrated that cell viability was maintained for 72 h in culture and that the tumor microenvironments and vascular integrities of the tissues were intact throughout the culture period. We then administered chemotherapeutics to assess drug responses and found differential sensitivity across different patient-derived tissues, enabling us to determine individualized medication plans. Overall, our study validated this rapid, cost-effective, scalable, and reproducible protocol for GC tissue culture that can be employed for drug response assessments. Our 3D culture platform paves a new way for personalized medication in GC and other tumors and can greatly impact future oncological research.
Keywords: apoptosis; chemotherapy effectiveness; ex vivo tumor tissue culture; gastric cancer; proliferation.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Chen, Hu, Zhu, Luo, Wang, Wang, Sun, Chen, Xie, Lou, Huang, Li, Xu, Xue and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- China NHCotPsRo . Standards for gastric cancer diagnosis and treatment (2018 edition). Multi Cancer Treat (2019) 5(1):55–82. 10.12151/JMCM.2019.01-08 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

