Whole-genome Identification of Transcriptional Start Sites by Differential RNA-seq in Bacteria
- PMID: 33659416
- PMCID: PMC7842792
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3757
Whole-genome Identification of Transcriptional Start Sites by Differential RNA-seq in Bacteria
Abstract
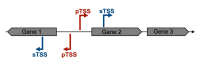
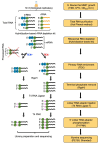
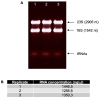
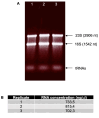
Gene transcription in bacteria often starts some nucleotides upstream of the start codon. Identifying the specific Transcriptional Start Site (TSS) is essential for genetic manipulation, as in many cases upstream of the start codon there are sequence elements that are involved in gene expression regulation. Taken into account the classical gene structure, we are able to identify two kinds of transcriptional start site: primary and secondary. A primary transcriptional start site is located some nucleotides upstream of the translational start site, while a secondary transcriptional start site is located within the gene encoding sequence. Here, we present a step by step protocol for genome-wide transcriptional start sites determination by differential RNA-sequencing (dRNA-seq) using the enteric pathogen Shigella flexneri serotype 5a strain M90T as model. However, this method can be employed in any other bacterial species of choice. In the first steps, total RNA is purified from bacterial cultures using the hot phenol method. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is specifically depleted via hybridization probes using a commercial kit. A 5'-monophosphate-dependent exonuclease (TEX)-treated RNA library enriched in primary transcripts is then prepared for comparison with a library that has not undergone TEX-treatment, followed by ligation of an RNA linker adaptor of known sequence allowing the determination of TSS with single nucleotide precision. Finally, the RNA is processed for Illumina sequencing library preparation and sequenced as purchased service. TSS are identified by in-house bioinformatic analysis. Our protocol is cost-effective as it minimizes the use of commercial kits and employs freely available software.
Keywords: 5′-monophosphate-dependent exonuclease (TEX); Bacterial gene regulation; Hot phenol RNA extraction; Phenol chloroform:isoamyl alcohol RNA extraction; RNA phosphorylation; RNA precipitation; RNA purification; TSS; Transcriptional start site; dRNA-seq; rRNA depletion.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Beckmann B. M., Burenina O. Y., Hoch P. G., Kubareva E. A., Sharma C. M. and Hartmann R. K.(2011). In vivo and in vitro analysis of 6S RNA-templated short transcripts in Bacillus subtilis . RNA Biol 8(5): 839-849. - PubMed
-
- Berghoff B. A., Glaeser J., Sharma C. M., Vogel J. and Klug G.(2009). Photooxidative stress-induced and abundant small RNAs in Rhodobacter sphaeroides . Mol Microbiol 74(6): 1497-1512. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

